Page 183 - Geotechnical Engineering Soil and Foundation Principles and Practice
P. 183
Soil Fabric and Structure
178 Geotechnical Engineering
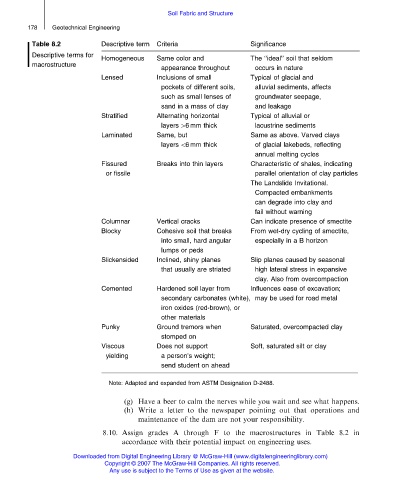
Table 8.2 Descriptive term Criteria Significance
Descriptive terms for
Homogeneous Same color and The ‘‘ideal’’ soil that seldom
macrostructure
appearance throughout occurs in nature
Lensed Inclusions of small Typical of glacial and
pockets of different soils, alluvial sediments, affects
such as small lenses of groundwater seepage,
sand in a mass of clay and leakage
Stratified Alternating horizontal Typical of alluvial or
layers 46 mm thick lacustrine sediments
Laminated Same, but Same as above. Varved clays
layers 56 mm thick of glacial lakebeds, reflecting
annual melting cycles
Fissured Breaks into thin layers Characteristic of shales, indicating
or fissile parallel orientation of clay particles
The Landslide Invitational.
Compacted embankments
can degrade into clay and
fail without warning
Columnar Vertical cracks Can indicate presence of smectite
Blocky Cohesive soil that breaks From wet-dry cycling of smectite,
into small, hard angular especially in a B horizon
lumps or peds
Slickensided Inclined, shiny planes Slip planes caused by seasonal
that usually are striated high lateral stress in expansive
clay. Also from overcompaction
Cemented Hardened soil layer from Influences ease of excavation;
secondary carbonates (white), may be used for road metal
iron oxides (red-brown), or
other materials
Punky Ground tremors when Saturated, overcompacted clay
stomped on
Viscous Does not support Soft, saturated silt or clay
yielding a person’s weight;
send student on ahead
Note: Adapted and expanded from ASTM Designation D-2488.
(g) Have a beer to calm the nerves while you wait and see what happens.
(h) Write a letter to the newspaper pointing out that operations and
maintenance of the dam are not your responsibility.
8.10. Assign grades A through F to the macrostructures in Table 8.2 in
accordance with their potential impact on engineering uses.
Downloaded from Digital Engineering Library @ McGraw-Hill (www.digitalengineeringlibrary.com)
Copyright © 2007 The McGraw-Hill Companies. All rights reserved.
Any use is subject to the Terms of Use as given at the website.