Page 226 - Geotechnical Engineering Soil and Foundation Principles and Practice
P. 226
Pore Water Pressure, Capillary Water, and Frost Action
Pore Water Pressure, Capillary Water, and Frost Action 221
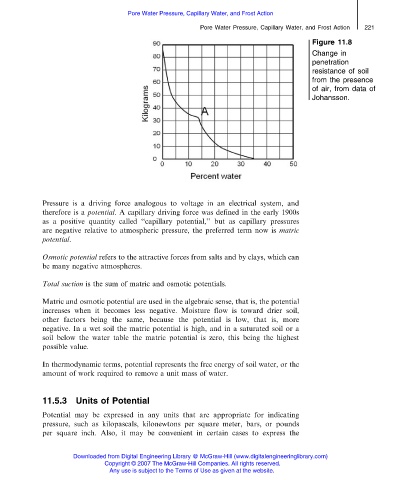
Figure 11.8
Change in
penetration
resistance of soil
from the presence
of air, from data of
Johansson.
Pressure is a driving force analogous to voltage in an electrical system, and
therefore is a potential. A capillary driving force was defined in the early 1900s
as a positive quantity called ‘‘capillary potential,’’ but as capillary pressures
are negative relative to atmospheric pressure, the preferred term now is matric
potential.
Osmotic potential refers to the attractive forces from salts and by clays, which can
be many negative atmospheres.
Total suction is the sum of matric and osmotic potentials.
Matric and osmotic potential are used in the algebraic sense, that is, the potential
increases when it becomes less negative. Moisture flow is toward drier soil,
other factors being the same, because the potential is low, that is, more
negative. In a wet soil the matric potential is high, and in a saturated soil or a
soil below the water table the matric potential is zero, this being the highest
possible value.
In thermodynamic terms, potential represents the free energy of soil water, or the
amount of work required to remove a unit mass of water.
11.5.3 Units of Potential
Potential may be expressed in any units that are appropriate for indicating
pressure, such as kilopascals, kilonewtons per square meter, bars, or pounds
per square inch. Also, it may be convenient in certain cases to express the
Downloaded from Digital Engineering Library @ McGraw-Hill (www.digitalengineeringlibrary.com)
Copyright © 2007 The McGraw-Hill Companies. All rights reserved.
Any use is subject to the Terms of Use as given at the website.