Page 233 - Geotechnical Engineering Soil and Foundation Principles and Practice
P. 233
Pore Water Pressure, Capillary Water, and Frost Action
228 Geotechnical Engineering
or the point of zero potential, will always be at the saturation moisture content
of the soil. Several instruments based on this principle are described by Fredlund
and Rahardjo (1993).
A limitation of a tensiometer is that tension cannot exceed 1 atmosphere because
water vapor bubbles will form in the porous cup so that the instrument is no
longer operative. Nevertheless, this device offers many possibilities for studying
soil-moisture changes within its range of applicability.
11.7.3 Zero-Point Translation Devices
In order to avoid cavitation of water in a tensiometer, the entire system can be put
under pressure. The most common method for doing this is to place saturated soil
specimens on a porous ceramic plate that is saturated with water and has
sufficient capillary retention that it does not allow entry of air (Fig. 11.13). Then
air pressure is applied to push water out of the soil and into the plate. Equilibrium
will be reached at a particular differential pressure that represents the matric
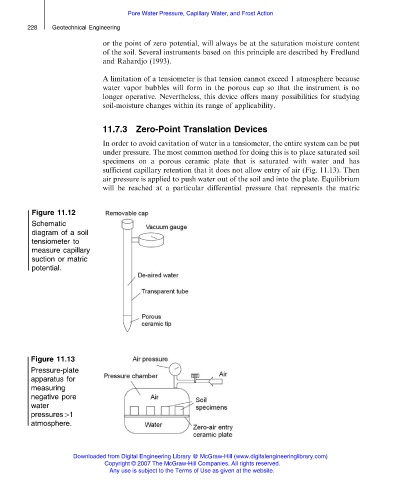
Figure 11.12
Schematic
diagram of a soil
tensiometer to
measure capillary
suction or matric
potential.
Figure 11.13
Pressure-plate
apparatus for
measuring
negative pore
water
pressures41
atmosphere.
Downloaded from Digital Engineering Library @ McGraw-Hill (www.digitalengineeringlibrary.com)
Copyright © 2007 The McGraw-Hill Companies. All rights reserved.
Any use is subject to the Terms of Use as given at the website.