Page 66 - Geotechnical Engineering Soil and Foundation Principles and Practice
P. 66
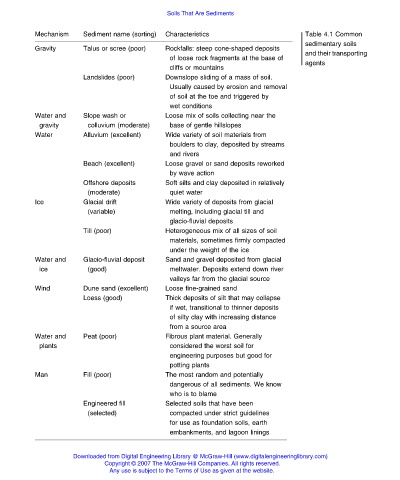
Soils That Are Sediments
Mechanism Sediment name (sorting) Characteristics Table 4.1 Common
sedimentary soils
Gravity Talus or scree (poor) Rockfalls: steep cone-shaped deposits
and their transporting
of loose rock fragments at the base of
agents
cliffs or mountains
Landslides (poor) Downslope sliding of a mass of soil.
Usually caused by erosion and removal
of soil at the toe and triggered by
wet conditions
Water and Slope wash or Loose mix of soils collecting near the
gravity colluvium (moderate) base of gentle hillslopes
Water Alluvium (excellent) Wide variety of soil materials from
boulders to clay, deposited by streams
and rivers
Beach (excellent) Loose gravel or sand deposits reworked
by wave action
Offshore deposits Soft silts and clay deposited in relatively
(moderate) quiet water
Ice Glacial drift Wide variety of deposits from glacial
(variable) melting, including glacial till and
glacio-fluvial deposits
Till (poor) Heterogeneous mix of all sizes of soil
materials, sometimes firmly compacted
under the weight of the ice
Water and Glacio-fluvial deposit Sand and gravel deposited from glacial
ice (good) meltwater. Deposits extend down river
valleys far from the glacial source
Wind Dune sand (excellent) Loose fine-grained sand
Loess (good) Thick deposits of silt that may collapse
if wet, transitional to thinner deposits
of silty clay with increasing distance
from a source area
Water and Peat (poor) Fibrous plant material. Generally
plants considered the worst soil for
engineering purposes but good for
potting plants
Man Fill (poor) The most random and potentially
dangerous of all sediments. We know
who is to blame
Engineered fill Selected soils that have been
(selected) compacted under strict guidelines
for use as foundation soils, earth
embankments, and lagoon linings
Downloaded from Digital Engineering Library @ McGraw-Hill (www.digitalengineeringlibrary.com)
Copyright © 2007 The McGraw-Hill Companies. All rights reserved.
Any use is subject to the Terms of Use as given at the website.