Page 302 - Global Project Management Handbook
P. 302
PROJECT QUALITY MANAGEMENT IN INTERNATIONAL PROJECTS 15-3
Services that are a part of the project or services that support the project need to be
considered in planning an international project. Training in the operation or use of
equipment is an example of where services may be required. Translation of documents
or translations of an individual’s oral report could be another area for consideration in
the service-support area.
PLANNING FOR QUALITY IN INTERNATIONAL PROJECTS
Because modern quality management is a prevention-oriented function that calls for
anticipating requirements, planning is a major consideration. Planning requires that a
person define the future product and visualize how it will be built. As in all environ-
ments, the project manager as the primary quality leader must set the standards for
quality and ensure they are met through both comprehensive plans and follow-through
on the actual build and testing of the products.
Planning for quality takes on many aspects of defining the product in terms that are
understood by the performing parties and that these parties have the capability to meet
the specified levels of workmanship. Some examples and areas for consideration in
international project quality are detailed here with brief explanations.
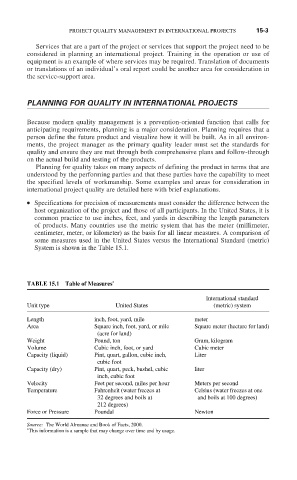
● Specifications for precision of measurements must consider the difference between the
host organization of the project and those of all participants. In the United States, it is
common practice to use inches, feet, and yards in describing the length parameters
of products. Many countries use the metric system that has the meter (millimeter,
centimeter, meter, or kilometer) as the basis for all linear measures. A comparison of
some measures used in the United States versus the International Standard (metric)
System is shown in the Table 15.1.
∗
TABLE 15.1 Table of Measures
International standard
Unit type (metric) system
United States
Length inch, foot, yard, mile meter
Area Square inch, foot, yard, or mile Square meter (hectare for land)
(acre for land)
Weight Pound, ton Gram, kilogram
Volume Cubic inch, foot, or yard Cubic meter
Capacity (liquid) Pint, quart, gallon, cubic inch, Liter
cubic foot
Capacity (dry) Pint, quart, peck, bushel, cubic liter
inch, cubic foot
Velocity Feet per second, miles per hour Meters per second
Temperature Fahrenheit (water freezes at Celsius (water freezes at one
32 degrees and boils at and boils at 100 degrees)
212 degrees)
Force or Pressure Poundal Newton
Source: The World Almanac and Book of Facts, 2000.
∗
This information is a sample that may change over time and by usage.