Page 104 -
P. 104
C C o o l i n g o o l i n g 75 75
C
C h a p t e r 4 : h a p t e r 4 :
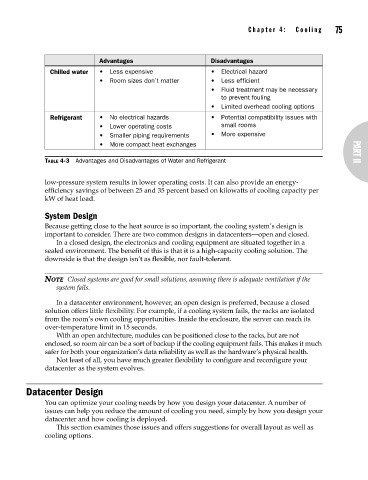
Advantages Disadvantages
Chilled water • Less expensive • Electrical hazard
• Room sizes don’t matter • Less efficient
• Fluid treatment may be necessary
to prevent fouling
• Limited overhead cooling options
Refrigerant • No electrical hazards • Potential compatibility issues with
• Lower operating costs small rooms
• Smaller piping requirements • More expensive
• More compact heat exchanges
TABLE 4-3 Advantages and Disadvantages of Water and Refrigerant PART II
low-pressure system results in lower operating costs. It can also provide an energy-
efficiency savings of between 25 and 35 percent based on kilowatts of cooling capacity per
kW of heat load.
System Design
Because getting close to the heat source is so important, the cooling system’s design is
important to consider. There are two common designs in datacenters—open and closed.
In a closed design, the electronics and cooling equipment are situated together in a
sealed environment. The benefit of this is that it is a high-capacity cooling solution. The
downside is that the design isn’t as flexible, nor fault-tolerant.
NOTE Closed systems are good for small solutions, assuming there is adequate ventilation if the
system fails.
In a datacenter environment, however, an open design is preferred, because a closed
solution offers little flexibility. For example, if a cooling system fails, the racks are isolated
from the room’s own cooling opportunities. Inside the enclosure, the server can reach its
over-temperature limit in 15 seconds.
With an open architecture, modules can be positioned close to the racks, but are not
enclosed, so room air can be a sort of backup if the cooling equipment fails. This makes it much
safer for both your organization’s data reliability as well as the hardware’s physical health.
Not least of all, you have much greater flexibility to configure and reconfigure your
datacenter as the system evolves.
Datacenter Design
You can optimize your cooling needs by how you design your datacenter. A number of
issues can help you reduce the amount of cooling you need, simply by how you design your
datacenter and how cooling is deployed.
This section examines those issues and offers suggestions for overall layout as well as
cooling options.