Page 68 -
P. 68
C
C h a p t e r 2 : h a p t e r 2 : C C u r r e n t I n i t i a t i v e s a n d S t a n d a r d s u r r e n t I n i t i a t i v e s a n d S t a n d a r d s 39 39
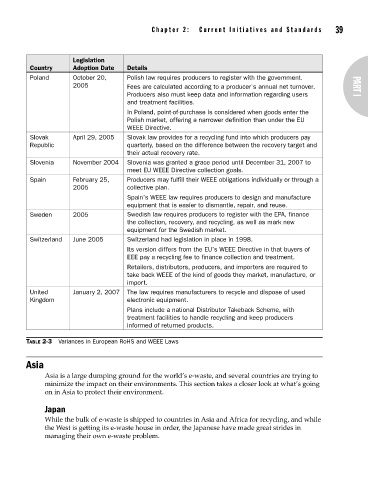
Legislation
Country Adoption Date Details
Poland October 20, Polish law requires producers to register with the government.
2005 Fees are calculated according to a producer’s annual net turnover. PART I
Producers also must keep data and information regarding users
PART I
PART I
and treatment facilities.
In Poland, point-of-purchase is considered when goods enter the
Polish market, offering a narrower definition than under the EU
WEEE Directive.
Slovak April 29, 2005 Slovak law provides for a recycling fund into which producers pay
Republic quarterly, based on the difference between the recovery target and
their actual recovery rate.
Slovenia November 2004 Slovenia was granted a grace period until December 31, 2007 to
meet EU WEEE Directive collection goals.
Spain February 25, Producers may fulfill their WEEE obligations individually or through a
2005 collective plan.
Spain’s WEEE law requires producers to design and manufacture
equipment that is easier to dismantle, repair, and reuse.
Sweden 2005 Swedish law requires producers to register with the EPA, finance
the collection, recovery, and recycling, as well as mark new
equipment for the Swedish market.
Switzerland June 2005 Switzerland had legislation in place in 1998.
Its version differs from the EU’s WEEE Directive in that buyers of
EEE pay a recycling fee to finance collection and treatment.
Retailers, distributors, producers, and importers are required to
take back WEEE of the kind of goods they market, manufacture, or
import.
United January 2, 2007 The law requires manufacturers to recycle and dispose of used
Kingdom electronic equipment.
Plans include a national Distributor Takeback Scheme, with
treatment facilities to handle recycling and keep producers
informed of returned products.
TABLE 2-3 Variances in European RoHS and WEEE Laws
Asia
Asia is a large dumping ground for the world’s e-waste, and several countries are trying to
minimize the impact on their environments. This section takes a closer look at what’s going
on in Asia to protect their environment.
Japan
While the bulk of e-waste is shipped to countries in Asia and Africa for recycling, and while
the West is getting its e-waste house in order, the Japanese have made great strides in
managing their own e-waste problem.