Page 98 -
P. 98
C C o o l i n g o o l i n g 69 69
C h a p t e r 4 : h a p t e r 4 :
C
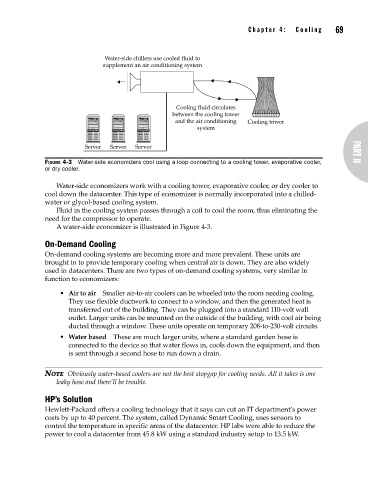
Water-side chillers use cooled fluid to
supplement an air conditioning system
Cooling fluid circulates
between the cooling tower
and the air conditioning Cooling tower
system
Server Server Server PART II
FIGURE 4-3 Water-side economizers cool using a loop connecting to a cooling tower, evaporative cooler,
or dry cooler.
Water-side economizers work with a cooling tower, evaporative cooler, or dry cooler to
cool down the datacenter. This type of economizer is normally incorporated into a chilled-
water or glycol-based cooling system.
Fluid in the cooling system passes through a coil to cool the room, thus eliminating the
need for the compressor to operate.
A water-side economizer is illustrated in Figure 4-3.
On-Demand Cooling
On-demand cooling systems are becoming more and more prevalent. These units are
brought in to provide temporary cooling when central air is down. They are also widely
used in datacenters. There are two types of on-demand cooling systems, very similar in
function to economizers:
• Air to air Smaller air-to-air coolers can be wheeled into the room needing cooling.
They use flexible ductwork to connect to a window, and then the generated heat is
transferred out of the building. They can be plugged into a standard 110-volt wall
outlet. Larger units can be mounted on the outside of the building, with cool air being
ducted through a window. These units operate on temporary 208-to-230-volt circuits.
• Water based These are much larger units, where a standard garden hose is
connected to the device so that water flows in, cools down the equipment, and then
is sent through a second hose to run down a drain.
NOTE Obviously water-based coolers are not the best stopgap for cooling needs. All it takes is one
leaky hose and there’ll be trouble.
HP’s Solution
Hewlett-Packard offers a cooling technology that it says can cut an IT department’s power
costs by up to 40 percent. The system, called Dynamic Smart Cooling, uses sensors to
control the temperature in specific areas of the datacenter. HP labs were able to reduce the
power to cool a datacenter from 45.8 kW using a standard industry setup to 13.5 kW.