Page 298 - Handbook of Thermal Analysis of Construction Materials
P. 298
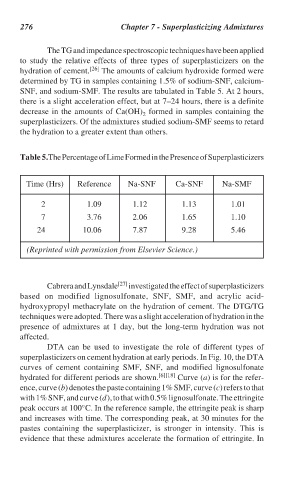
276 Chapter 7 - Superplasticizing Admixtures
The TG and impedance spectroscopic techniques have been applied
to study the relative effects of three types of superplasticizers on the
hydration of cement. [26] The amounts of calcium hydroxide formed were
determined by TG in samples containing 1.5% of sodium-SNF, calcium-
SNF, and sodium-SMF. The results are tabulated in Table 5. At 2 hours,
there is a slight acceleration effect, but at 7–24 hours, there is a definite
decrease in the amounts of Ca(OH) formed in samples containing the
2
superplasticizers. Of the admixtures studied sodium-SMF seems to retard
the hydration to a greater extent than others.
Table 5. The Percentage of Lime Formed in the Presence of Superplasticizers
Time (Hrs) Reference Na-SNF Ca-SNF Na-SMF
2 1.09 1.12 1.13 1.01
7 3.76 2.06 1.65 1.10
24 10.06 7.87 9.28 5.46
(Reprinted with permission from Elsevier Science.)
Cabrera and Lynsdale [27] investigated the effect of superplasticizers
based on modified lignosulfonate, SNF, SMF, and acrylic acid-
hydroxypropyl methacrylate on the hydration of cement. The DTG/TG
techniques were adopted. There was a slight acceleration of hydration in the
presence of admixtures at 1 day, but the long-term hydration was not
affected.
DTA can be used to investigate the role of different types of
superplasticizers on cement hydration at early periods. In Fig. 10, the DTA
curves of cement containing SMF, SNF, and modified lignosulfonate
hydrated for different periods are shown. [6][18] Curve (a) is for the refer-
ence, curve (b) denotes the paste containing 1% SMF, curve (c) refers to that
with 1% SNF, and curve (d), to that with 0.5% lignosulfonate. The ettringite
peak occurs at 100°C. In the reference sample, the ettringite peak is sharp
and increases with time. The corresponding peak, at 30 minutes for the
pastes containing the superplasticizer, is stronger in intensity. This is
evidence that these admixtures accelerate the formation of ettringite. In