Page 318 - Handbook of Thermal Analysis of Construction Materials
P. 318
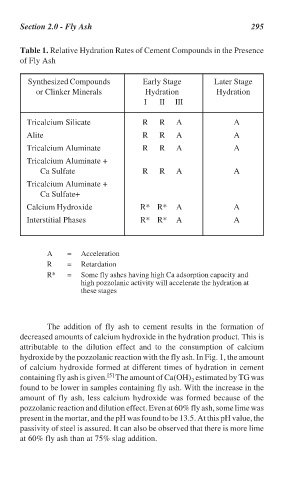
Section 2.0 - Fly Ash 295
Table 1. Relative Hydration Rates of Cement Compounds in the Presence
of Fly Ash
Synthesized Compounds Early Stage Later Stage
or Clinker Minerals Hydration Hydration
I II III
Tricalcium Silicate R R A A
Alite R R A A
Tricalcium Aluminate R R A A
Tricalcium Aluminate +
Ca Sulfate R R A A
Tricalcium Aluminate +
Ca Sulfate+
Calcium Hydroxide R* R* A A
Interstitial Phases R* R* A A
A = Acceleration
R = Retardation
R* = Some fly ashes having high Ca adsorption capacity and
high pozzolanic activity will accelerate the hydration at
these stages
The addition of fly ash to cement results in the formation of
decreased amounts of calcium hydroxide in the hydration product. This is
attributable to the dilution effect and to the consumption of calcium
hydroxide by the pozzolanic reaction with the fly ash. In Fig. 1, the amount
of calcium hydroxide formed at different times of hydration in cement
[5]
containing fly ash is given. The amount of Ca(OH) estimated by TG was
2
found to be lower in samples containing fly ash. With the increase in the
amount of fly ash, less calcium hydroxide was formed because of the
pozzolanic reaction and dilution effect. Even at 60% fly ash, some lime was
present in the mortar, and the pH was found to be 13.5. At this pH value, the
passivity of steel is assured. It can also be observed that there is more lime
at 60% fly ash than at 75% slag addition.