Page 76 - Handbook of Thermal Analysis of Construction Materials
P. 76
Section 10.0 - Mathematical Models 59
paste, non-evaporable water, heat evolution, strength, porosity, permeabil-
ity, etc. Garboczi and Bentz [25] describe the computer-based model of
microstructure and properties as “…a theoretical construct, which is made
using valid scientific principles expressed in mathematical language, that
can be used to make quantitative prediction about a material’s structure
and/or properties.” The computer-based model is, thus, used to numeri-
cally represent the amount and spatial distribution of different phases of the
material being studied and, thus, predict from the numerical representa-
tion of microstructure, properties that can be derived from actual experi-
ments. Simulation of the interfacial zone model has also been carried out.
Details of the application of the models have been reviewed recently. [26][27]
These models also have to consider that the properties of concrete depend
on the fine structure of C-S-H as well as that of coarse aggregate. It is also
important to determine the microstructural characteristics of the material as
it deforms due to rheology, creep, shrinkage, and fracture.
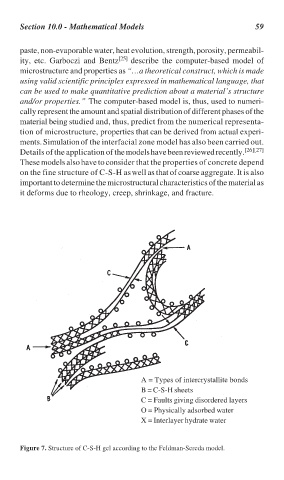
A = Types of intercrystallite bonds
B = C-S-H sheets
C = Faults giving disordered layers
O = Physically adsorbed water
X = Interlayer hydrate water
Figure 7. Structure of C-S-H gel according to the Feldman-Sereda model.