Page 233 - Geology and Geochemistry of Oil and Gas
P. 233
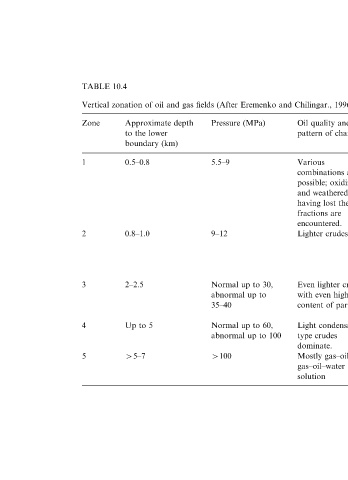
TABLE 10.4 202
Vertical zonation of oil and gas fields (After Eremenko and Chilingar., 1996, p.125.)
Zone Approximate depth Pressure (MPa) Oil quality and Mutual solubility of Drive mechanism Gas composition in
to the lower pattern of changes oil and gas gas accumulations
boundary (km)
1 0.5–0.8 5.5–9 Various Direct correlation. Combination of any Dry gas dominates.
combinations are Associated gas drives is possible.
possible; oxidized becomes dryer with
and weathered crudes depth.
having lost their light
fractions are
encountered. CLASSIFICATIONS
2 0.8–1.0 9–12 Lighter crudes Weak inverse Water drive is Percentage of wet gas
solubility is possible common in oil increases.
depending on the oil accumulations.
and gas quality. Elastic drive is also
observed. OF
3 2–2.5 Normal up to 30, Even lighter crudes Inverse solubility Water and depletion Condensate is OIL
abnormal up to with even higher becomes clearer with (elastic) drives are common.
35–40 content of paraffins depth. Gas becomes most common. AND
more wet.
4 Up to 5 Normal up to 60, Light condensate- Same as above Same as above Condensate is always GAS
abnormal up to 100 type crudes present
dominate.
5 45–7 4100 Mostly gas–oil or Single phase Elastic drive Gas–oil–water
gas–oil–water solution
solution ACCUMULATIONS