Page 144 - Hacking Roomba
P. 144
Chapter 6 — Reading the Roomba Sensors 125
Accurate Readings
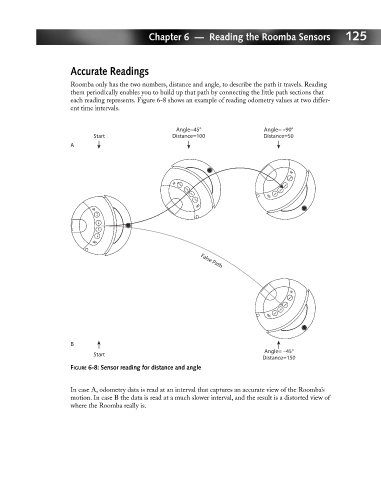
Roomba only has the two numbers, distance and angle, to describe the path it travels. Reading
them periodically enables you to build up that path by connecting the little path sections that
each reading represents. Figure 6-8 shows an example of reading odometry values at two differ-
ent time intervals.
Angle=45° Angle= –90°
Start Distance=100 Distance=50
A status
status
power
clean
spot
max
dirt detect False Path detect dirt max spot clean power
status
power
clean
spot
max
dirt
detect
B detect dirt max spot clean power status
Angle= –45°
Start
Distance=150
FIGURE 6-8: Sensor reading for distance and angle
In case A, odometry data is read at an interval that captures an accurate view of the Roomba’s
motion. In case B the data is read at a much slower interval, and the result is a distorted view of
where the Roomba really is.