Page 209 - Handbook Of Multiphase Flow Assurance
P. 209
Cold flow and emulsion 207
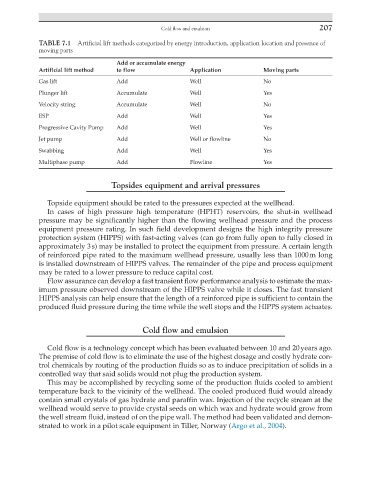
TABLE 7.1 Artificial lift methods categorized by energy introduction, application location and presence of
moving parts
Add or accumulate energy
Artificial lift method to flow Application Moving parts
Gas lift Add Well No
Plunger lift Accumulate Well Yes
Velocity string Accumulate Well No
ESP Add Well Yes
Progressive Cavity Pump Add Well Yes
Jet pump Add Well or flowline No
Swabbing Add Well Yes
Multiphase pump Add Flowline Yes
Topsides equipment and arrival pressures
Topside equipment should be rated to the pressures expected at the wellhead.
In cases of high pressure high temperature (HPHT) reservoirs, the shut-in wellhead
pressure may be significantly higher than the flowing wellhead pressure and the process
equipment pressure rating. In such field development designs the high integrity pressure
protection system (HIPPS) with fast-acting valves (can go from fully open to fully closed in
approximately 3 s) may be installed to protect the equipment from pressure. A certain length
of reinforced pipe rated to the maximum wellhead pressure, usually less than 1000 m long
is installed downstream of HIPPS valves. The remainder of the pipe and process equipment
may be rated to a lower pressure to reduce capital cost.
Flow assurance can develop a fast transient flow performance analysis to estimate the max-
imum pressure observed downstream of the HIPPS valve while it closes. The fast transient
HIPPS analysis can help ensure that the length of a reinforced pipe is sufficient to contain the
produced fluid pressure during the time while the well stops and the HIPPS system actuates.
Cold flow and emulsion
Cold flow is a technology concept which has been evaluated between 10 and 20 years ago.
The premise of cold flow is to eliminate the use of the highest dosage and costly hydrate con-
trol chemicals by routing of the production fluids so as to induce precipitation of solids in a
controlled way that said solids would not plug the production system.
This may be accomplished by recycling some of the production fluids cooled to ambient
temperature back to the vicinity of the wellhead. The cooled produced fluid would already
contain small crystals of gas hydrate and paraffin wax. Injection of the recycle stream at the
wellhead would serve to provide crystal seeds on which wax and hydrate would grow from
the well stream fluid, instead of on the pipe wall. The method had been validated and demon-
strated to work in a pilot scale equipment in Tiller, Norway (Argo et al., 2004).