Page 402 - Handbook of Thermal Analysis of Construction Materials
P. 402
Section 6.0 - Phosphate Cement Systems 379
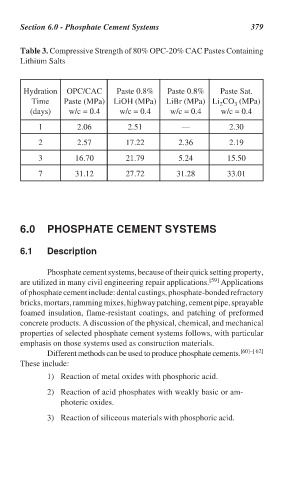
Table 3. Compressive Strength of 80% OPC-20% CAC Pastes Containing
Lithium Salts
Hydration OPC/CAC Paste 0.8% Paste 0.8% Paste Sat.
Time Paste (MPa) LiOH (MPa) LiBr (MPa) Li CO (MPa)
2
3
(days) w/c = 0.4 w/c = 0.4 w/c = 0.4 w/c = 0.4
1 2.06 2.51 — 2.30
2 2.57 17.22 2.36 2.19
3 16.70 21.79 5.24 15.50
7 31.12 27.72 31.28 33.01
6.0 PHOSPHATE CEMENT SYSTEMS
6.1 Description
Phosphate cement systems, because of their quick setting property,
are utilized in many civil engineering repair applications. [59] Applications
of phosphate cement include: dental castings, phosphate-bonded refractory
bricks, mortars, ramming mixes, highway patching, cement pipe, sprayable
foamed insulation, flame-resistant coatings, and patching of preformed
concrete products. A discussion of the physical, chemical, and mechanical
properties of selected phosphate cement systems follows, with particular
emphasis on those systems used as construction materials.
Different methods can be used to produce phosphate cements. [60]–[ 62]
These include:
1) Reaction of metal oxides with phosphoric acid.
2) Reaction of acid phosphates with weakly basic or am-
photeric oxides.
3) Reaction of siliceous materials with phosphoric acid.