Page 548 - Handbook of Thermal Analysis of Construction Materials
P. 548
Section 3.0 - Applications 517
3.8 Solid Waste in Clay Bricks
The possibility of using Aswan clay combined with industrial
waste products, e.g., blast-furnace slag and air-water cooled converter slag,
has been investigated with the assistance of thermal analysis. [29] The results
show that the substitution of 10% clay by blast-furnace slag fired at 900 and
1000°C improves the compressive strength and the bulk density, but the
substitution by converter slag decreases these properties. The results of
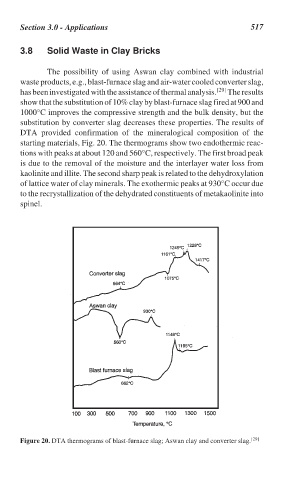
DTA provided confirmation of the mineralogical composition of the
starting materials, Fig. 20. The thermograms show two endothermic reac-
tions with peaks at about 120 and 560°C, respectively. The first broad peak
is due to the removal of the moisture and the interlayer water loss from
kaolinite and illite. The second sharp peak is related to the dehydroxylation
of lattice water of clay minerals. The exothermic peaks at 930°C occur due
to the recrystallization of the dehydrated constituents of metakaolinite into
spinel.
Figure 20. DTA thermograms of blast-furnace slag; Aswan clay and converter slag. [29]