Page 546 - Handbook of Adhesives and Sealants
P. 546
Sealant Classification and Composition 471
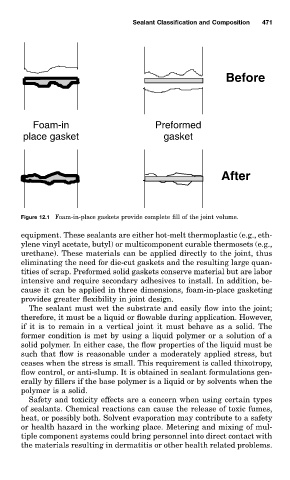
Before
Foam-in Preformed
place gasket gasket
After
Figure 12.1 Foam-in-place gaskets provide complete fill of the joint volume.
equipment. These sealants are either hot-melt thermoplastic (e.g., eth-
ylene vinyl acetate, butyl) or multicomponent curable thermosets (e.g.,
urethane). These materials can be applied directly to the joint, thus
eliminating the need for die-cut gaskets and the resulting large quan-
tities of scrap. Preformed solid gaskets conserve material but are labor
intensive and require secondary adhesives to install. In addition, be-
cause it can be applied in three dimensions, foam-in-place gasketing
provides greater flexibility in joint design.
The sealant must wet the substrate and easily flow into the joint;
therefore, it must be a liquid or flowable during application. However,
if it is to remain in a vertical joint it must behave as a solid. The
former condition is met by using a liquid polymer or a solution of a
solid polymer. In either case, the flow properties of the liquid must be
such that flow is reasonable under a moderately applied stress, but
ceases when the stress is small. This requirement is called thixotropy,
flow control, or anti-slump. It is obtained in sealant formulations gen-
erally by fillers if the base polymer is a liquid or by solvents when the
polymer is a solid.
Safety and toxicity effects are a concern when using certain types
of sealants. Chemical reactions can cause the release of toxic fumes,
heat, or possibly both. Solvent evaporation may contribute to a safety
or health hazard in the working place. Metering and mixing of mul-
tiple component systems could bring personnel into direct contact with
the materials resulting in dermatitis or other health related problems.