Page 357 - Handbook of Battery Materials
P. 357
11.2 Separators for Lead–Acid Storage Batteries 327
silicas, which fixes the sulfuric acid solution molecules by van der Waals bonds
within a lattice. These gels have thixotropic properties; that is, by mechanical
stirring they can be liquefied and used to fill into the battery cells, where they gel
again within a few minutes. Initially such batteries suffer some water loss during
overcharge. The gel dries to some extent and forms cracks, allowing the oxygen to
transfer to the negative electrode where the internal oxygen consumption occurs,
which avoids further water loss and gel drying [20, 21, 105, 106].
Batteries with gelled electrolyte have been shown to require a separator, in the
conventional sense, to secure spacing of the electrodes as well as to prevent any
electronic shorts; the latter is achieved by microporous separators. An additional
important criterion is minimal acid displacement, since these batteries – in com-
parison with batteries with liquid electrolyte – lack the electrolyte volume share
taken up by gelling and by the cracks.
Among the separator varieties described, the phenol–formaldehyde–resorcinol
separator (DARAK 2000) [60] as well as the microporous PVC separator [85] have
proven effective for this construction. For applications without deep discharges,
concessions may be made with the respect to porosity and pore sizes of the separator;
therefore polyethylene separators or a special version of glass leaf separators with
attached glass mat [72] are occasionally used in such cases.
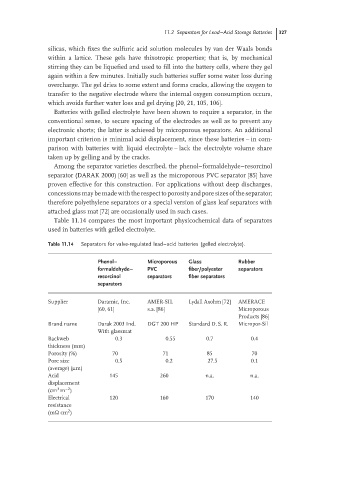
Table 11.14 compares the most important physicochemical data of separators
used in batteries with gelled electrolyte.
Table 11.14 Separators for valve-regulated lead–acid batteries (gelled electrolyte).
Phenol– Microporous Glass Rubber
formaldehyde– PVC fiber/polyester separators
resorcinol separators fiber separators
separators
Supplier Daramic, Inc. AMER-SIL Lydall Axohm [72] AMERACE
[60, 61] s.a. [86] Microporous
Products [86]
Brand name Darak 2003 Ind. DGT 200 HP Standard D. S. R. Micropor-Sil
With glassmat
Backweb 0.3 0.55 0.7 0.4
thickness (mm)
Porosity (%) 70 71 85 70
Pore size 0.5 0.2 27.5 0.1
(average) (µm)
Acid 145 260 n.a. n.a.
displacement
3
–2
(cm m )
Electrical 120 160 170 140
resistance
2
(m cm )