Page 108 - Handbook of Deep Learning in Biomedical Engineering Techniques and Applications
P. 108
96 Chapter 4 A critical review on using blockchain technology in education domain
3.2 Vote-based approaches
These approaches are based on the Byzantine general problem. A
consensus is to be reached between Byzantine generals over the
attack strategy with the assumption that some generals may be
traitors and try to adopt treacherous actions to prevent loyal
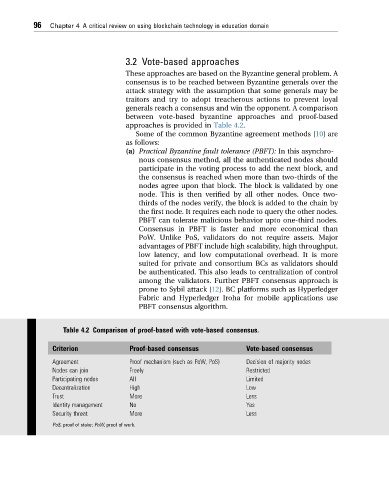
generals reach a consensus and win the opponent. A comparison
between vote-based byzantine approaches and proof-based
approaches is provided in Table 4.2.
Some of the common Byzantine agreement methods [10] are
as follows:
(a) Practical Byzantine fault tolerance (PBFT): In this asynchro-
nous consensus method, all the authenticated nodes should
participate in the voting process to add the next block, and
the consensus is reached when more than two-thirds of the
nodes agree upon that block. The block is validated by one
node. This is then verified by all other nodes. Once two-
thirds of the nodes verify, the block is added to the chain by
the first node. It requires each node to query the other nodes.
PBFT can tolerate malicious behavior upto one-third nodes.
Consensus in PBFT is faster and more economical than
PoW. Unlike PoS, validators do not require assets. Major
advantages of PBFT include high scalability, high throughput,
low latency, and low computational overhead. It is more
suited for private and consortium BCs as validators should
be authenticated. This also leads to centralization of control
among the validators. Further PBFT consensus approach is
prone to Sybil attack [12]. BC platforms such as Hyperledger
Fabric and Hyperledger Iroha for mobile applications use
PBFT consensus algorithm.
Table 4.2 Comparison of proof-based with vote-based consensus.
Criterion Proof-based consensus Vote-based consensus
Agreement Proof mechanism (such as PoW, PoS) Decision of majority nodes
Nodes can join Freely Restricted
Participating nodes All Limited
Decentralization High Low
Trust More Less
Identity management No Yes
Security threat More Less
PoS, proof of stake; PoW, proof of work.