Page 84 - Handbook of Electronic Assistive Technology
P. 84
Chapter 3 • Functional Posture 71
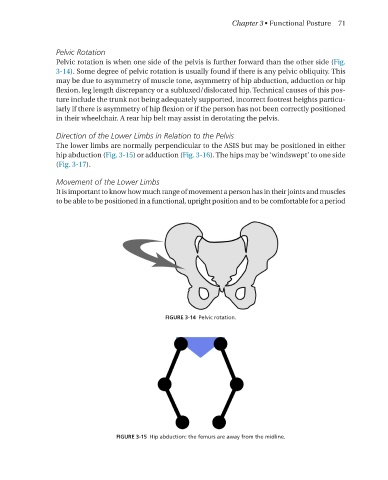
Pelvic Rotation
Pelvic rotation is when one side of the pelvis is further forward than the other side (Fig.
3-14). Some degree of pelvic rotation is usually found if there is any pelvic obliquity. This
may be due to asymmetry of muscle tone, asymmetry of hip abduction, adduction or hip
flexion, leg length discrepancy or a subluxed/dislocated hip. Technical causes of this pos-
ture include the trunk not being adequately supported, incorrect footrest heights particu-
larly if there is asymmetry of hip flexion or if the person has not been correctly positioned
in their wheelchair. A rear hip belt may assist in derotating the pelvis.
Direction of the Lower Limbs in Relation to the Pelvis
The lower limbs are normally perpendicular to the ASIS but may be positioned in either
hip abduction (Fig. 3-15) or adduction (Fig. 3-16). The hips may be ‘windswept’ to one side
(Fig. 3-17).
Movement of the Lower Limbs
It is important to know how much range of movement a person has in their joints and muscles
to be able to be positioned in a functional, upright position and to be comfortable for a period
FIGURE 3-14 Pelvic rotation�
FIGURE 3-15 Hip abduction: the femurs are away from the midline�