Page 113 - Handbook of Energy Engineering Calculations
P. 113
3. Apply the heat-rate and heater-number correction factors
Full-load regenerative-cycle heat rate, Btu/kWh = (straight-condensing heat
rate, Btu/kWh) [1 − (heat-rate correction factor) (heater-number correction
factor)] = (13,350)[1 − (0.148)(0.71)] = 10,160 Btu/kWh (10,719.4 kJ/kWh).
4. Find and apply the correction factors for the larger number of heaters
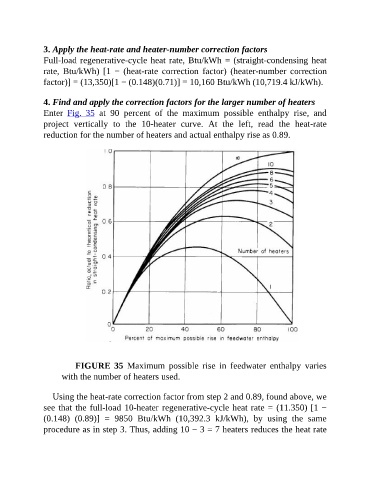
Enter Fig. 35 at 90 percent of the maximum possible enthalpy rise, and
project vertically to the 10-heater curve. At the left, read the heat-rate
reduction for the number of heaters and actual enthalpy rise as 0.89.
FIGURE 35 Maximum possible rise in feedwater enthalpy varies
with the number of heaters used.
Using the heat-rate correction factor from step 2 and 0.89, found above, we
see that the full-load 10-heater regenerative-cycle heat rate = (11.350) [1 −
(0.148) (0.89)] = 9850 Btu/kWh (10,392.3 kJ/kWh), by using the same
procedure as in step 3. Thus, adding 10 − 3 = 7 heaters reduces the heat rate