Page 110 - Handbook of Gold Exploration and Evaluation
P. 110
90 Handbook of gold exploration and evaluation
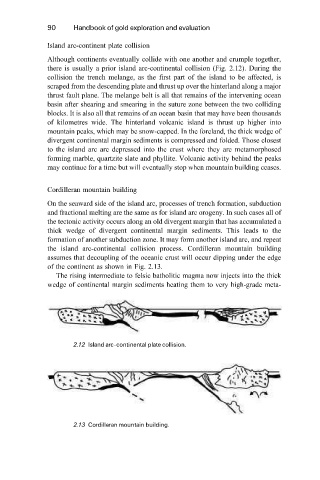
Island arc-continent plate collision
Although continents eventually collide with one another and crumple together,
there is usually a prior island arc-continental collision (Fig. 2.12). During the
collision the trench melange, as the first part of the island to be affected, is
scraped from the descending plate and thrust up over the hinterland along a major
thrust fault plane. The melange belt is all that remains of the intervening ocean
basin after shearing and smearing in the suture zone between the two colliding
blocks. It is also all that remains of an ocean basin that may have been thousands
of kilometres wide. The hinterland volcanic island is thrust up higher into
mountain peaks, which may be snow-capped. In the foreland, the thick wedge of
divergent continental margin sediments is compressed and folded. Those closest
to the island arc are depressed into the crust where they are metamorphosed
forming marble, quartzite slate and phyllite. Volcanic activity behind the peaks
may continue for a time but will eventually stop when mountain building ceases.
Cordilleran mountain building
On the seaward side of the island arc, processes of trench formation, subduction
and fractional melting are the same as for island arc orogeny. In such cases all of
the tectonic activity occurs along an old divergent margin that has accumulated a
thick wedge of divergent continental margin sediments. This leads to the
formation of another subduction zone. It may form another island arc, and repeat
the island arc-continental collision process. Cordilleran mountain building
assumes that decoupling of the oceanic crust will occur dipping under the edge
of the continent as shown in Fig. 2.13.
The rising intermediate to felsic batholitic magma now injects into the thick
wedge of continental margin sediments heating them to very high-grade meta-
2.12 Island arc-continental plate collision.
2.13 Cordilleran mountain building.