Page 164 - Handbook of Gold Exploration and Evaluation
P. 164
142 Handbook of gold exploration and evaluation
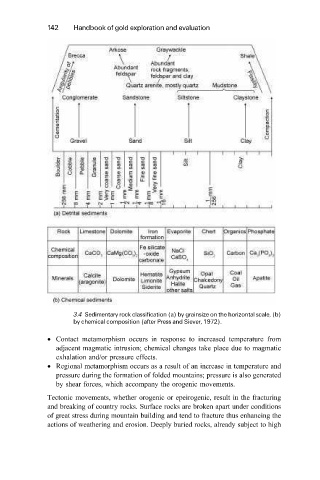
3.4 Sedimentary rock classification (a) by grainsize on the horizontal scale, (b)
by chemical composition (after Press and Siever, 1972).
· Contact metamorphism occurs in response to increased temperature from
adjacent magmatic intrusion; chemical changes take place due to magmatic
exhalation and/or pressure effects.
· Regional metamorphism occurs as a result of an increase in temperature and
pressure during the formation of folded mountains; pressure is also generated
by shear forces, which accompany the orogenic movements.
Tectonic movements, whether orogenic or epeirogenic, result in the fracturing
and breaking of country rocks. Surface rocks are broken apart under conditions
of great stress during mountain building and tend to fracture thus enhancing the
actions of weathering and erosion. Deeply buried rocks, already subject to high