Page 175 - Handbook of Gold Exploration and Evaluation
P. 175
Gold deposition in the weathering environment 153
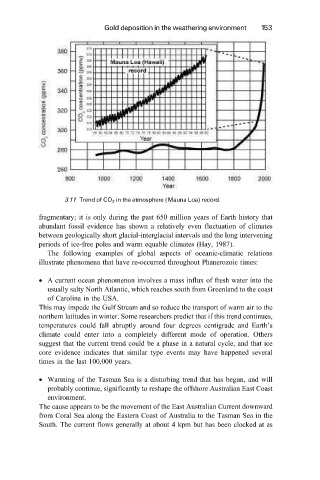
3.11 Trend of CO 2 in the atmosphere (Mauna Loa) record.
fragmentary; it is only during the past 650 million years of Earth history that
abundant fossil evidence has shown a relatively even fluctuation of climates
between geologically short glacial-interglacial intervals and the long intervening
periods of ice-free poles and warm equable climates (Hay, 1987).
The following examples of global aspects of oceanic-climatic relations
illustrate phenomena that have re-occurred throughout Phanerozoic times:
· A current ocean phenomenon involves a mass influx of fresh water into the
usually salty North Atlantic, which reaches south from Greenland to the coast
of Carolina in the USA.
This may impede the Gulf Stream and so reduce the transport of warm air to the
northern latitudes in winter. Some researchers predict that if this trend continues,
temperatures could fall abruptly around four degrees centigrade and Earth's
climate could enter into a completely different mode of operation. Others
suggest that the current trend could be a phase in a natural cycle, and that ice
core evidence indicates that similar type events may have happened several
times in the last 100,000 years.
· Warming of the Tasman Sea is a disturbing trend that has begun, and will
probably continue, significantly to reshape the offshore Australian East Coast
environment.
The cause appears to be the movement of the East Australian Current downward
from Coral Sea along the Eastern Coast of Australia to the Tasman Sea in the
South. The current flows generally at about 4 kpm but has been clocked at as