Page 272 - Handbook of Gold Exploration and Evaluation
P. 272
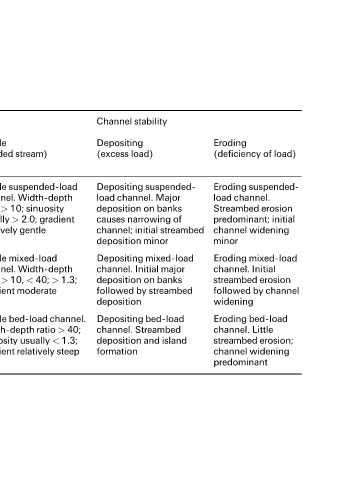
Table 4.5 Classification of alluvial channels (after Galloway, 1989)
Mode of sediment % silt and clay Bed-load Channel stability
transport and deposited in (percentage of
type of channel channel of total Stable Depositing Eroding
perimeter load) (graded stream) (excess load) (deficiency of load)
(m)
Suspended-load >20 <3 Stable suspended-load Depositing suspended- Eroding suspended-
channel. Width-depth load channel. Major load channel.
ratio > 10; sinuosity deposition on banks Streambed erosion
usually > 2.0; gradient causes narrowing of predominant; initial
relatively gentle channel; initial streambed channel widening
deposition minor minor
Mixed-load 5±20 3±11 Stable mixed-load Depositing mixed-load Eroding mixed-load
channel. Width-depth channel. Initial major channel. Initial
ratio > 10, < 40; > 1.3; deposition on banks streambed erosion
gradient moderate followed by streambed followed by channel
deposition widening
Bed-load <5 >11 Stable bed-load channel. Depositing bed-load Eroding bed-load
Width-depth ratio > 40; channel. Streambed channel. Little
sinuosity usually < 1.3; deposition and island streambed erosion;
gradient relatively steep formation channel widening
predominant