Page 180 -
P. 180
in-place or copied sorting
Sort in one of two ways
When it comes to sorting your data using Python, you have two options.
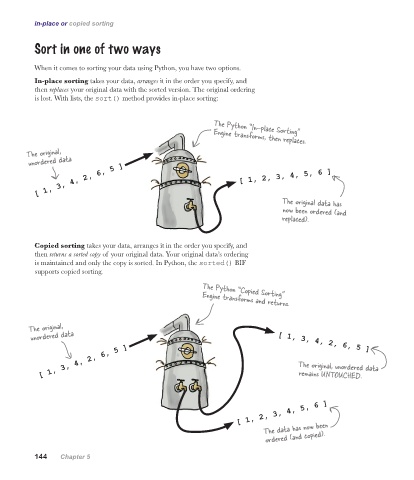
In-place sorting takes your data, arranges it in the order you specify, and
then replaces your original data with the sorted version. The original ordering
is lost. With lists, the sort() method provides in-place sorting:
The Python “In-place Sorting”
Engine transforms, then replaces.
The original,
unordered data
[ 1, 3, 4, 2, 6, 5 ] [ 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6 ]
The original data has
now been ordered (and
replaced).
Copied sorting takes your data, arranges it in the order you specify, and
then returns a sorted copy of your original data. Your original data’s ordering
is maintained and only the copy is sorted. In Python, the sorted() BIF
supports copied sorting.
The Python “Copied Sorting”
Engine transforms and returns.
The original,
unordered data [ 1, 3, 4, 2, 6, 5 ]
[ 1, 3, 4, 2, 6, 5 ] The original, unordered data
remains UNTOUCHED.
[ 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6 ]
The data has now been
ordered (and copied).
144 Chapter 5