Page 110 - High Power Laser Handbook
P. 110
80 G a s , C h e m i c a l , a n d F r e e - E l e c t r o n L a s e r s High-Power Fr ee-Electr on Lasers 81
Electron
x trajectory
z
E x
z
(a)
E x
z
(b)
Transverse E x
photonic
electric field z
at each
indicated (c)
location
E x
z
(d)
E x
z
(e)
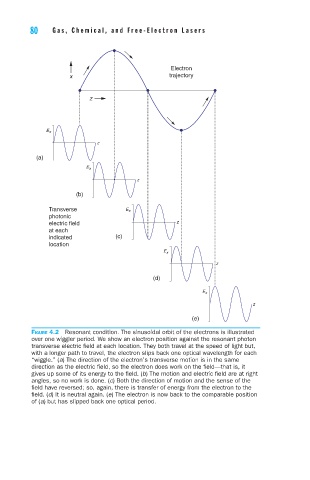
Figure 4.2 Resonant condition. The sinusoidal orbit of the electrons is illustrated
over one wiggler period. We show an electron position against the resonant photon
transverse electric field at each location. They both travel at the speed of light but,
with a longer path to travel, the electron slips back one optical wavelength for each
“wiggle.” (a) The direction of the electron’s transverse motion is in the same
direction as the electric field, so the electron does work on the field—that is, it
gives up some of its energy to the field. (b) The motion and electric field are at right
angles, so no work is done. (c) Both the direction of motion and the sense of the
field have reversed; so, again, there is transfer of energy from the electron to the
field. (d) It is neutral again. (e) The electron is now back to the comparable position
of (a) but has slipped back one optical period.