Page 448 - High Power Laser Handbook
P. 448
416 Fi b er L a s er s Intr oduction to Optical Fiber Lasers 417
and efficient absorption of the pump once coupled into a double-clad
optical fiber. A glass host also provides broader absorption and
emission spectra for rare earth ions due to strong inhomogeneous
broadening, leading to less constraint on pump wavelength stability,
a wider range of lasing wavelengths, and a wide gain bandwidth, all
of which are critical factors for ultrashort pulse lasers.
15.2 Rare-Earth-Doped Optical Fibers
15.2.1 Basics of Optical Fibers
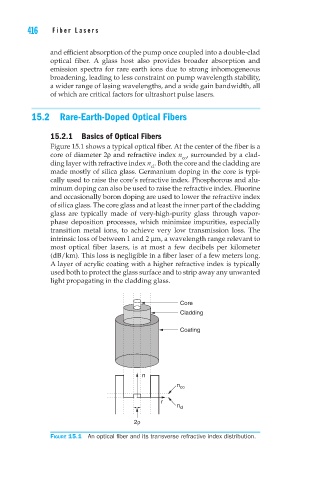
Figure 15.1 shows a typical optical fiber. At the center of the fiber is a
core of diameter 2ρ and refractive index n , surrounded by a clad-
co
ding layer with refractive index n . Both the core and the cladding are
cl
made mostly of silica glass. Germanium doping in the core is typi-
cally used to raise the core’s refractive index. Phosphorous and alu-
minum doping can also be used to raise the refractive index. Fluorine
and occasionally boron doping are used to lower the refractive index
of silica glass. The core glass and at least the inner part of the cladding
glass are typically made of very-high-purity glass through vapor-
phase deposition processes, which minimize impurities, especially
transition metal ions, to achieve very low transmission loss. The
intrinsic loss of between 1 and 2 µm, a wavelength range relevant to
most optical fiber lasers, is at most a few decibels per kilometer
(dB/km). This loss is negligible in a fiber laser of a few meters long.
A layer of acrylic coating with a higher refractive index is typically
used both to protect the glass surface and to strip away any unwanted
light propagating in the cladding glass.
Core
Cladding
Coating
n
n co
r
n cl
2ρ
Figure 15.1 An optical fiber and its transverse refractive index distribution.