Page 70 - Highway Engineering Handbook Building and Rehabilitating the Infrastructure
P. 70
ENVIRONMENTAL ISSUES 53
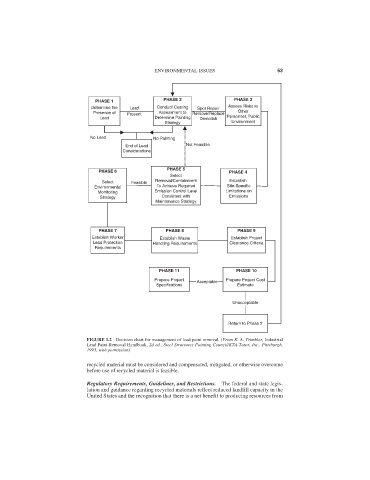
PHASE 1 PHASE 2 PHASE 3
Determine the Lead Conduct Coating Spot Repair Assess Risks to
Presence of Present Assessment to Remove/Replace Other
Lead Determine Painting Demolish Personnel, Public
Strategy Environment
No Lead No Painting
End of Lead Not Feasible
Considerations
PHASE 5
PHASE 6 PHASE 4
Select
Select Feasible Removal/Containment Establish
Environmental To Achieve Required Site-Specific
Monitoring Emission Control Level Limitations on
Strategy Consistent with Emissions
Maintenance Strategy
PHASE 7 PHASE 8 PHASE 9
Establish Worker Establish Waste Establish Project
Lead Protection Handling Requirements Clearance Criteria
Requirements
PHASE 11 PHASE 10
Prepare Project Acceptable Prepare Project Cost
Specifications Estimate
Unacceptable
Return to Phase 2
FIGURE 1.2 Decision chart for management of lead paint removal. (From K. A. Trimbler, Industrial
Lead Paint Removal Handbook, 2d ed., Steel Structures Painting Council/KTA-Tator, Inc., Pittsburgh,
1993, with permission)
recycled material must be considered and compensated, mitigated, or otherwise overcome
before use of recycled material is feasible.
Regulatory Requirements, Guidelines, and Restrictions. The federal and state legis-
lation and guidance regarding recycled materials reflect reduced landfill capacity in the
United States and the recognition that there is a net benefit to producing resources from