Page 356 - Industrial Ventilation Design Guidebook
P. 356
3 1 2 CHAPTER 5 PHYSIOLOGICAL AND TOXICOLOGICAL CONSIDERATIONS
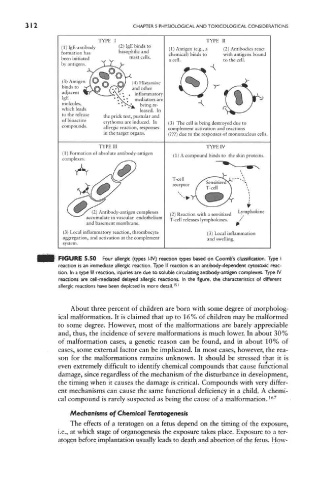
FIGURE 5.50 Four allergic (types I-IV) reaction types based on Coomb's classification. Type f
reaction is an immediate allergic reaction. Type II reaction is an antibody-dependent cytotoxic reac-
tion. In a type III reaction, injuries are due to soluble circulating antibody-antigen complexes. Type IV
reactions are cell-mediated delayed allergic reactions. In the figure, the characteristics of different
allergic reactions have been depicted in more detail. 151
About three percent of children are born with some degree of morpholog-
ical malformation. It is claimed that up to 16% of children may be malformed
to some degree. However, most of the malformations are barely appreciable
and, thus, the incidence of severe malformations is much lower. In about 30%
of malformation cases, a genetic reason can be found, and in about 10% of
cases, some external factor can be implicated. In most cases, however, the rea-
son for the malformations remains unknown. It should be stressed that it is
even extremely difficult to identify chemical compounds that cause functional
damage, since regardless of the mechanism of the disturbance in development,
the timing when it causes the damage is critical. Compounds with very differ-
ent mechanisms can cause the same functional deficiency in a child. A chemi-
cal compound is rarely suspected as being the cause of a malformation. J6?
Mechanisms of Chemical Terotogenes/s
The effects of a teratogen on a fetus depend on the timing of the exposure,
i.e., at which stage of organogenesis the exposure takes place. Exposure to a ter-
atogen before implantation usually leads to death and abortion of the fetus. How-