Page 115 - Industrial Wastewater Treatment, Recycling and Reuse
P. 115
Advanced Physico-chemical Methods of Treatment for Industrial Wastewaters 89
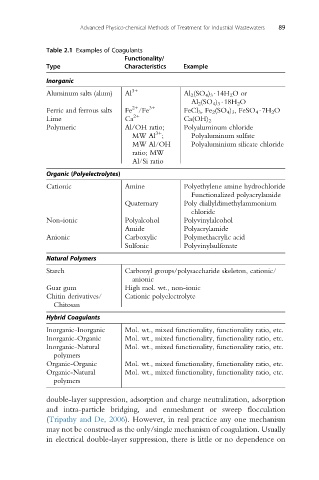
Table 2.1 Examples of Coagulants
Functionality/
Type Characteristics Example
Inorganic
Aluminum salts (alum) Al 3+ Al 2 (SO 4 ) 3 14H 2 Oor
Al 2 (SO 4 ) 3 18H 2 O
2+
Ferric and ferrous salts Fe /Fe 3+ FeCl 3 ,Fe 2 (SO 4 ) 3 , FeSO 4 7H 2 O
Lime Ca 2+ Ca(OH) 2
Polymeric Al/OH ratio; Polyaluminum chloride
3+
MW Al ; Polyaluminum sulfate
MW Al/OH Polyaluminium silicate chloride
ratio; MW
Al/Si ratio
Organic (Polyelectrolytes)
Cationic Amine Polyethylene amine hydrochloride
Functionalized polyacrylamide
Quaternary Poly diallyldimethylammonium
chloride
Non-ionic Polyalcohol Polyvinylalcohol
Amide Polyacrylamide
Anionic Carboxylic Polymethacrylic acid
Sulfonic Polyvinylsulfonate
Natural Polymers
Starch Carbonyl groups/polysaccharide skeleton, cationic/
anionic
Guar gum High mol. wt., non-ionic
Chitin derivatives/ Cationic polyelectrolyte
Chitosan
Hybrid Coagulants
Inorganic-Inorganic Mol. wt., mixed functionality, functionality ratio, etc.
Inorganic-Organic Mol. wt., mixed functionality, functionality ratio, etc.
Inorganic-Natural Mol. wt., mixed functionality, functionality ratio, etc.
polymers
Organic-Organic Mol. wt., mixed functionality, functionality ratio, etc.
Organic-Natural Mol. wt., mixed functionality, functionality ratio, etc.
polymers
double-layer suppression, adsorption and charge neutralization, adsorption
and intra-particle bridging, and enmeshment or sweep flocculation
(Tripathy and De, 2006). However, in real practice any one mechanism
may not be construed as the only/single mechanism of coagulation. Usually
in electrical double-layer suppression, there is little or no dependence on