Page 70 - Innovations in Intelligent Machines
P. 70
Team, Game, and Negotiation based UAV Task Allocation 59
the time taken to accomplish the mission is comparatively low. An expected
result of increase in performance with increase in sensor range can be seen
for the performance curves of negotiation scheme in the figure. However, this
intuitive result is not true for greedy strategy.
The performance of greedy strategy with sensor radius s r = 10 is better
than higher sensor radius s r =20 to s r = 50. This is due to the fact with low
sensor radius, the UAVs are unable to sense the targets initially and hence
move in the initial heading direction (spreading out). But, with higher sensor
radius, the agents are able to sense the target from their initial positions and
hence all the UAVs move in the direction of sensed target as a swarm. Hence,
the performance is worse when compared to lower sensor radius.
We carried out another set of simulations to study the performance of task
allocation algorithm for different target distributions on the search space. In
order to conduct these experiments we define a proximity factor that deter-
mines the nature of the distribution or spread of targets in the search space.
The proximity factor is defined as:
S r
ρ = (27)
1 N 2 2
N i=1 (x i − x c ) +(y i − y c )
where N is number of targets, (x i ,y i ) represents the position of the i th target
location, (x c ,y c ) the mean of all the target positions and S r the sensor radius.
Low proximity factor implies well separated targets compared to the sensor
radius. While high proximity factor ensures that the targets are placed very
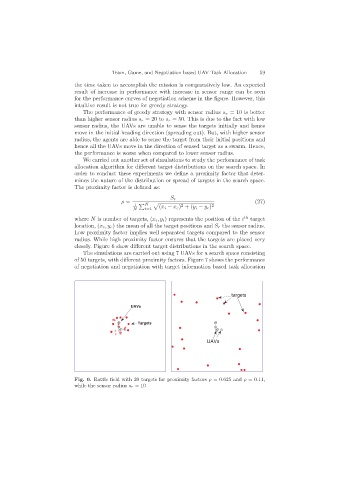
closely. Figure 6 show different target distributions in the search space.
The simulations are carried out using 7 UAVs for a search space consisting
of 50 targets, with different proximity factors. Figure 7 shows the performance
of negotiation and negotiation with target information based task allocation
targets
UAVs
Targets
UAVs
Fig. 6. Battle field with 20 targets for proximity factors ρ =0.625 and ρ =0.11,
while the sensor radius s r =10