Page 57 - Inorganic Mass Spectrometry - Fundamentals and Applications
P. 57
Glow Discharge Mass Spectrometry
t 22: 3t
Voltage characteristics versus time for pulsed direct current and radio fre-
quency discharges. (From Ref. 73.)
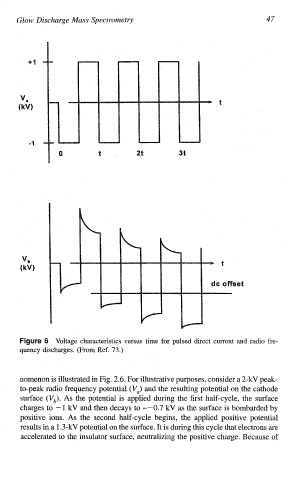
nomenon is illustrated in Fig. 2.6. For illustrative purposes, consider a 2-kV peak-
to-peak radio frequency potential (Va) and the resulting potential on the cathode
surface (Vb). As the potential is applied during the first half-cycle, the surface
charges to -1 kV and then decays to "-0.7 kV as the surface is bombarded by
positive ions. As the second half-cycle begins, the applied positive potential
results in a 1.3-kV potential on the surface. It is during this cycle that electrons are
accelerated to the insulator surface, neutralizing the positive charge. Because of