Page 63 - Instant notes
P. 63
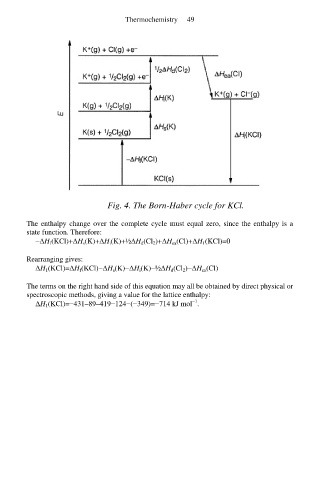
Thermochemistry 49
Fig. 4. The Born-Haber cycle for KCl.
The enthalpy change over the complete cycle must equal zero, since the enthalpy is a
state function. Therefore:
−∆H f(KCl)+∆H s(K)+∆H i(K)+½∆H d(Cl 2)+∆H ea(Cl)+∆H 1(KCl)=0
Rearranging gives:
∆H 1(KCl)=∆H f(KCl)−∆H s(K)−∆H i(K)−½∆H d(Cl 2)−∆H ea(Cl)
The terms on the right hand side of this equation may all be obtained by direct physical or
spectroscopic methods, giving a value for the lattice enthalpy:
−1
∆H 1(KCl)=−431–89–419−124−(−349)=−714 kJ mol .