Page 183 - Intelligent Digital Oil And Gas Fields
P. 183
140 Intelligent Digital Oil and Gas Fields
system. The objective is to minimize the overall life cycle cost of tools,
which includes the cost of maintenance and cost of failure. The optimization
variables are maintenance intervals and operational parameters such as RPM,
WOB, and ROP. Kale et al. (2015) have integrated qualification test data,
operational data, drilling dynamics, and historical FRACAS (Failure
reporting analysis and corrective action system) information with mathemat-
ical and statistical models—such as a proportional hazard model, cumulative
damage model, characteristic life function and maximum likelihood estima-
tion, and outlier detection—to predict the time to failure of critical compo-
nents. They validated the proposed methods to optimize maintenance
intervals of a rotary steerable system with and without a motor.
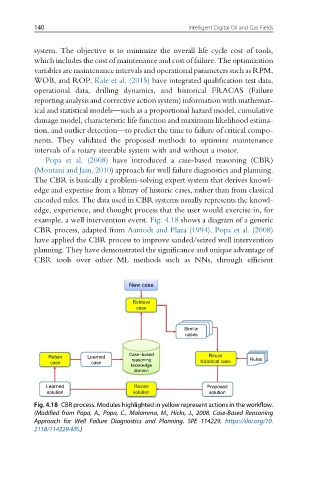
Popa et al. (2008) have introduced a case-based reasoning (CBR)
(Montani and Jain, 2010) approach for well failure diagnostics and planning.
The CBR is basically a problem-solving expert system that derives knowl-
edge and expertise from a library of historic cases, rather than from classical
encoded rules. The data used in CBR systems usually represents the knowl-
edge, experience, and thought process that the user would exercise in, for
example, a well intervention event. Fig. 4.18 shows a diagram of a generic
CBR process, adapted from Aamodt and Plaza (1994). Popa et al. (2008)
have applied the CBR process to improve sanded/seized well intervention
planning. They have demonstrated the significance and unique advantage of
CBR tools over other ML methods such as NNs, through efficient
New case
Retrieve
case
Similar
cases
Case–based
Retain Learned Reuse Rules
case case reasoning historical case
knowledge
domain
Learned Revise Proposed
solution solution solution
Fig. 4.18 CBR process. Modules highlighted in yellow represent actions in the workflow.
(Modified from Popa, A., Popa, C., Malamma, M., Hicks, J., 2008. Case-Based Reasoning
Approach for Well Failure Diagnostics and Planning. SPE 114229, https://doi.org/10.
2118/114229-MS.)