Page 381 - Intro Predictive Maintenance
P. 381
372 An Introduction to Predictive Maintenance
end pushing the side of the pencil with one finger. At the same time, push in the
opposite direction at the other end. The pencil will tend to rotate end-over-end. This
end-over-end action causes two imbalance “orbits,” both 180 degrees out-of-phase,
resulting in a “wobble” motion.
Balancing Standards. The International Standards Organization (ISO) has published
standards for acceptable limits for residual imbalance in various classifications of rotor
assemblies. Balancing standards are given in ounce-inches or pound-inches per pound
of rotor weight or the equivalent in metric units (g-mm/kg). The ounce-inches are for
each correction plane for which the imbalance is measured and corrected.
Caution must be exercised when using balancing standards. The recommended levels
are for residual imbalance, which is defined as imbalance of any kind that remains
after balancing. Table 16–2 is the norm established for most rotating equipment. Addi-
tional information can be obtained from ISO 5406 and 5343. Similar standards are
available from the American National Standards Institute (ANSI) in their publication
ANSI S2.43-1984.
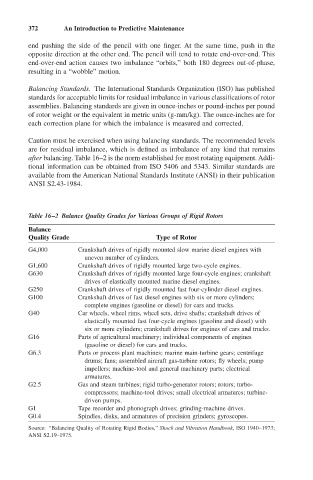
Table 16–2 Balance Quality Grades for Various Groups of Rigid Rotors
Balance
Quality Grade Type of Rotor
G4,000 Crankshaft drives of rigidly mounted slow marine diesel engines with
uneven number of cylinders.
G1,600 Crankshaft drives of rigidly mounted large two-cycle engines.
G630 Crankshaft drives of rigidly mounted large four-cycle engines; crankshaft
drives of elastically mounted marine diesel engines.
G250 Crankshaft drives of rigidly mounted fast four-cylinder diesel engines.
G100 Crankshaft drives of fast diesel engines with six or more cylinders;
complete engines (gasoline or diesel) for cars and trucks.
G40 Car wheels, wheel rims, wheel sets, drive shafts; crankshaft drives of
elastically mounted fast four-cycle engines (gasoline and diesel) with
six or more cylinders; crankshaft drives for engines of cars and trucks.
G16 Parts of agricultural machinery; individual components of engines
(gasoline or diesel) for cars and trucks.
G6.3 Parts or process plant machines; marine main-turbine gears; centrifuge
drums; fans; assembled aircraft gas-turbine rotors; fly wheels; pump
impellers; machine-tool and general machinery parts; electrical
armatures.
G2.5 Gas and steam turbines; rigid turbo-generator rotors; rotors; turbo-
compressors; machine-tool drives; small electrical armatures; turbine-
driven pumps.
G1 Tape recorder and phonograph drives; grinding-machine drives.
G0.4 Spindles, disks, and armatures of precision grinders; gyroscopes.
Source: “Balancing Quality of Rotating Rigid Bodies,” Shock and Vibration Handbook, ISO 1940–1973;
ANSI S2.19–1975.