Page 39 - Intro Predictive Maintenance
P. 39
30 An Introduction to Predictive Maintenance
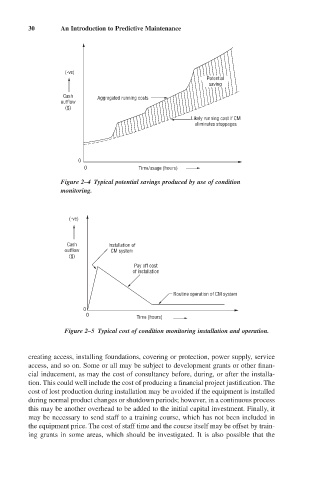
(-ve)
Potential
saving
Cash Aggregated running costs
outflow
( ) S
Likely running cost if CM
eliminates stoppages
0
0 Time/usage (hours)
Figure 2–4 Typical potential savings produced by use of condition
monitoring.
(-ve)
Cash Installation of
outflow CM system
( ) S
Pay off cost
of installation
Routine operation of CM system
0
0
Time (hours)
Figure 2–5 Typical cost of condition monitoring installation and operation.
creating access, installing foundations, covering or protection, power supply, service
access, and so on. Some or all may be subject to development grants or other finan-
cial inducement, as may the cost of consultancy before, during, or after the installa-
tion. This could well include the cost of producing a financial project justification. The
cost of lost production during installation may be avoided if the equipment is installed
during normal product changes or shutdown periods; however, in a continuous process
this may be another overhead to be added to the initial capital investment. Finally, it
may be necessary to send staff to a training course, which has not been included in
the equipment price. The cost of staff time and the course itself may be offset by train-
ing grants in some areas, which should be investigated. It is also possible that the