Page 106 - Intro to Space Sciences Spacecraft Applications
P. 106
Spacecraft Environment
93
er descriptions of the atmospheric regions. As it stands, there is a thermal
balance between the amount of energy absorbed and the amount reradiat-
ed into space, but the above discussion shows the concern over increasing
the carbon dioxide levels in the atmosphere as can happen through the
large-scale burning of fossil fuels and forests.*
Particle Interactions
To discuss the characteristics of the solar particle radiations in the
vicinity of the earth, we must first discuss the earth’s own magnetic field
and the interaction of charged particles with this field.
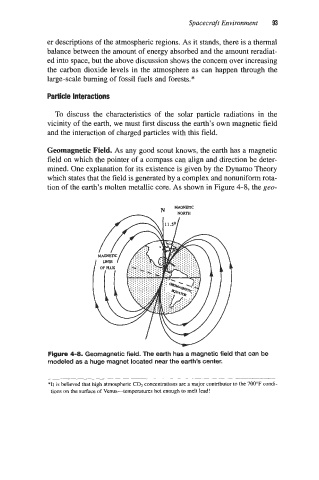
Geomagnetic Field. As any good scout knows, the earth has a magnetic
field on which the pointer of a compass can align and direction be deter-
mined. One explanation for its existence is given by the Dynamo Theory
which states that the field is generated by a complex and nonuniform rota-
tion of the earth’s molten metallic core. As shown in Figure 4-8, the geo-
Figure 4-8. Geomagnetic field. The earth has a magnetic field that can be
modeled as a huge magnet located near the earth’s center.
*It is believed that high atmospheric COz concentrations are a major contributor to the 700°F condi-
tions on the surface of Venus-temperatures hot enough to melt lead!