Page 205 - Intro to Space Sciences Spacecraft Applications
P. 205
Introduction to Space Sciences and Spacecraft Applications
192
one iteration to the next. By this process, all subsystems take into account
the mass of each of the other subsystems in their mass computations.
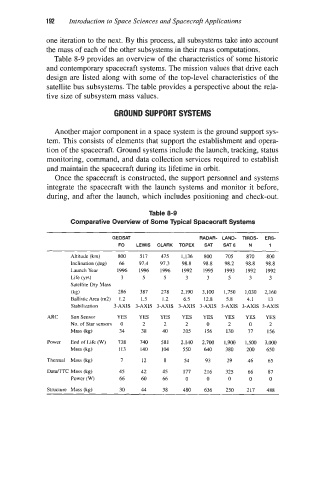
Table 8-9 provides an overview of the characteristics of some historic
and contemporary spacecraft systems. The mission values that drive each
design are listed along with some of the top-level characteristics of the
satellite bus subsystems. The table provides a perspective about the rela-
tive size of subsystem mass values.
GROUND SUPPORT SYSTEMS
Another major component in a space system is the ground support sys-
tem. This consists of elements that support the establishment and opera-
tion of the spacecraft. Ground systems include the launch, tracking, status
monitoring, command, and data collection services required to establish
and maintain the spacecraft during its lifetime in orbit.
Once the spacecraft is constructed, the support personnel and systems
integrate the spacecraft with the launch systems and monitor it before,
during, and after the launch, which includes positioning and check-out.
Table 8-9
Comparative Overview of Some Typical Spacecraft Systems
GEOSAT RADAR- LAND- mos- ERS-
FO LEWIS CLARK TOPEX SAT SAT6 N 1
Altitude (km) 800 517 475 1,136 800 705 870 800
Inclination (deg) 66 97.4 97.3 98.8 98.8 98.2 98.8 98.8
Launch Year 1996 1996 1996 1992 1995 1993 1992 1992
Life (yrs) 3 5 5 3 3 5 3 3
Satellite Dry Mass
(kg) 286 387 278 2,190 3,100 1,750 1,030 2,160
Ballistic Area (m2) 1.2 1.5 1.2 6.5 12.8 5.8 4.1 13
Stabilization 3-AXIS 3-AXIS 3-AXIS 3-AXIS 3-AXIS 3-AXIS 3-AXIS 3-AXIS
ARC Sun Sensor YES YES YES YES YES YES YES YES
No. of Star sensors 0 2 2 2 0 2 0 2
Mas (kg) 34 38 40 205 156 130 77 156
Power Endof Life(W) 738 740 581 2,140 2,700 1,900 1,500 3,000
Mass (kg) 113 140 104 550 640 380 200 650
Thermal Mass (kg) 7 12 8 54 93 29 46 65
DatflTC Mass (kg) 45 42 45 177 216 325 66 87
Power (W) 66 60 66 0 0 0 0 0
Structure Mass (kg) 30 44 38 480 636 250 217 488