Page 72 - Introduction to AI Robotics
P. 72
2.4 Representative Architectures
Mission 55
Planner
SENSE PLAN
Navigator
World
Model/
Knowledge
Base Pilot
Low-level ACT
Controller
sensors
sensors sensors drive steer
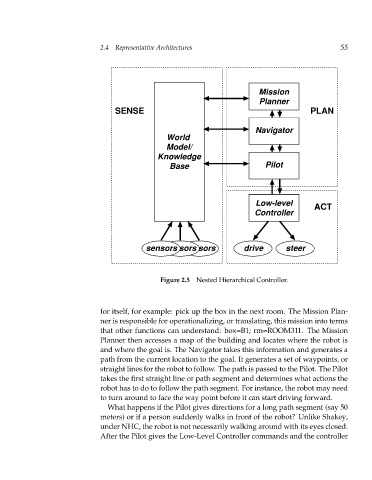
Figure 2.5 Nested Hierarchical Controller.
for itself, for example: pick up the box in the next room. The Mission Plan-
ner is responsible for operationalizing, or translating, this mission into terms
that other functions can understand: box=B1; rm=ROOM311. The Mission
Planner then accesses a map of the building and locates where the robot is
and where the goal is. The Navigator takes this information and generates a
path from the current location to the goal. It generates a set of waypoints, or
straight lines for the robot to follow. The path is passed to the Pilot. The Pilot
takes the first straight line or path segment and determines what actions the
robot has to do to follow the path segment. For instance, the robot may need
to turn around to face the way point before it can start driving forward.
What happens if the Pilot gives directions for a long path segment (say 50
meters) or if a person suddenly walks in front of the robot? Unlike Shakey,
under NHC, the robot is not necessarily walking around with its eyes closed.
After the Pilot gives the Low-Level Controller commands and the controller