Page 355 - Introduction to Continuum Mechanics
P. 355
Problems 330
538. Determine the total elongation of a steel bar 76 cm long if the tensile stress is 0.1 GPa
andEy =207GPa.
5.39. A cast iron bar, 4 ft (122 cm) long and 1.5 in.(3.81 cm) in diameter is pulled by equal and
opposite axial forces P at its ends.
(a) Find the maximum normal and shearing stresses if P = 20,000 Ib (89000 N).
6
(b) Find the total elongation and lateral contraction ( Ey- 15x10 psi (103 GPa),
v = 0.25).
2
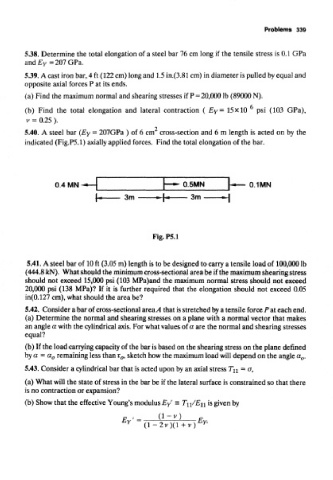
5.40. A steel bar (Ey - 207GPa ) of 6 cm cross-section and 6 m length is acted on by the
indicated (Fig.P5.1) axially applied forces. Find the total elongation of the bar.
Fig. P5.1
5.41. A steel bar of 10 ft (3.05 m) length is to be designed to carry a tensile load of 100,000 Ib
(444.8 kN). What should the minimum cross-sectional area be if the maximum shearing stress
should not exceed 15,000 psi (103 MPa)and the maximum normal stress should not exceed
20,000 psi (138 MPa)? If it is further required that the elongation should not exceed 0.05
in(0.127 cm), what should the area be?
5.42. Consider a bar of cross-sectional areayl that is stretched by a tensile force P at each end.
(a) Determine the normal and shearing stresses on a plane with a normal vector that makes
an angle a with the cylindrical axis. For what values of a are the normal and shearing stresses
equal?
(b) If the load carrying capacity of the bar is based on the shearing stress on the plane defined
by a = a 0 remaining less than r 0, sketch how the maximum load will depend on the angle a 0.
5.43. Consider a cylindrical bar that is acted upon by an axial stress TU = o,
(a) What will the state of stress in the bar be if the lateral surface is constrained so that there
is no contraction or expansion?
(b) Show that the effective Young's modulus Ey = TU/EU is given by