Page 461 - Introduction to Continuum Mechanics
P. 461
Principle of Linear Momentum 445
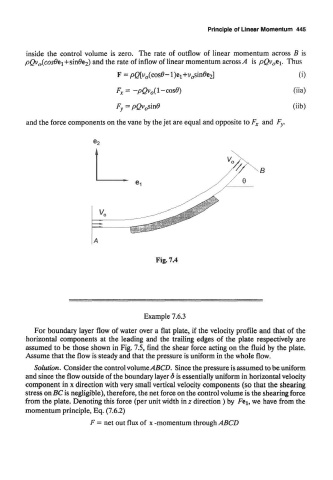
inside the control volume is zero. The rate of outflow of linear momentum across B is
p£)v 0(c0s0ei+sin#C2) and the rate of inflow of linear momentum across A is pQv 0t\. Thus
and the force components on the vane by the jet are equal and opposite to F x and F y,
Fig. 7.4
Example 7.6.3
For boundary layer flow of water over a flat plate, if the velocity profile and that of the
horizontal components at the leading and the trailing edges of the plate respectively are
assumed to be those shown in Fig. 7.5, find the shear force acting on the fluid by the plate.
Assume that the flow is steady and that the pressure is uniform in the whole flow.
Solution. Consider the control volumes-SCO. Since the pressure is assumed to be uniform
and since the flow outside of the boundary layer d is essentially uniform in horizontal velocity
component in x direction with very small vertical velocity components (so that the shearing
stress on BC is negligible), therefore, the net force on the control volume is the shearing force
from the plate. Denoting this force (per unit width in z direction) by Fei, we have from the
momentum principle, Eq. (7.6.2)
F = net out flux of x -momentum through ABCD