Page 472 - Introduction to Continuum Mechanics
P. 472
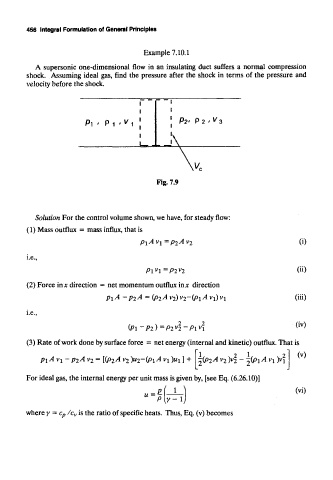
456 Integral Formulation of General Principles
Example 7.10.1
A supersonic one-dimensional flow in an insulating duct suffers a normal compression
shock. Assuming ideal gas, find the pressure after the shock in terms of the pressure and
velocity before the shock.
Fig. 7.9
Solution For the control volume shown, we have, for steady flow:
(1) Mass outflux = mass influx, that is
i.e.,
(2) Force in* direction = net momentum outflux in* direction
i.e.,
(3) Rate of work done by surface force = net energy (internal and kinetic) outflux. That is
For ideal gas, the internal energy per unit mass is given by, [see Eq. (6.26.10)}
where y = c p /c v is the ratio of specific heats. Thus, Eq. (v) becomes