Page 66 - Introduction to Continuum Mechanics
P. 66
Part C Scalar Field, Gradient of a Scalar Function 51
Example 2C2.2
If q denotes the heat flux vector (rate of heat flow/area), the Fourier heat conduction law
states that
q = -kVO
"7 *7
where Q is the temperature field and k is the thermal conductivity. If 6=2(xi+X2), find 6 at
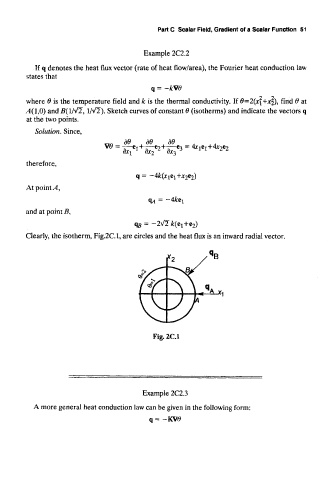
,4(1,0) and J?(1/V2", 1/vT). Sketch curves of constant 0 (isotherms) and indicate the vectors q
at the two points,
Solution, Since,
therefore,
At points,
and at point B,
Clearly, the isotherm, Fig.2C.l, are circles and the heat flux is an inward radial vector.
Fig.2C.l
Example 2C2.3
A more general heat conduction law can be given in the following form:
q= -KV0