Page 146 - Introduction to Electronic Commerce and Social Commerce
P. 146
126 4 Business-to-Business E-Commerce
applications. An example would be a manufacturer who is with its suppliers, designers, and other business partners, as
collaborating electronically with an engineering company well as with its customers and possibly the government. The
that designs a product or a part for the manufacturer. major elements of the collaboration process are illustrated in
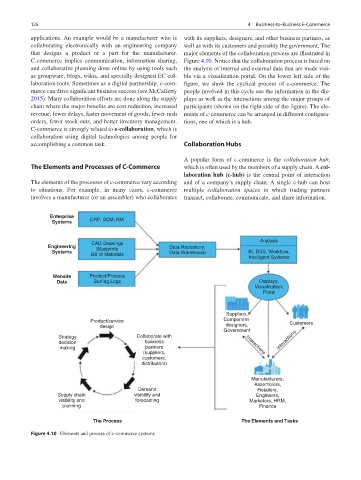
C-commerce implies communication, information sharing, Figure 4.10. Notice that the collaboration process is based on
and collaborative planning done online by using tools such the analysis of internal and external data that are made visi-
as groupware, blogs, wikis, and specially designed EC col- ble via a visualization portal. On the lower left side of the
laboration tools. Sometimes as a digital partnership, c-com- figure, we show the cyclical process of c-commerce. The
merce can drive significant business success (see McCafferty people involved in this cycle use the information in the dis-
2015). Many collaboration efforts are done along the supply plays as well as the interactions among the major groups of
chain where the major benefits are cost reduction, increased participants (shown on the right side of the figure). The ele-
revenue, fewer delays, faster movement of goods, fewer rush ments of c-commerce can be arranged in different configura-
orders, fewer stock-outs, and better inventory management. tions, one of which is a hub.
C-commerce is strongly related to e-collaboration, which is
collaboration using digital technologies among people for
accomplishing a common task. Collaboration Hubs
A popular form of c-commerce is the collaboration hub,
The Elements and Processes of C-Commerce which is often used by the members of a supply chain. A col-
laboration hub (c-hub) is the central point of interaction
The elements of the processes of c-commerce vary according and of a company’s supply chain. A single e-hub can host
to situations. For example, in many cases, c-commerce multiple collaboration spaces in which trading partners
involves a manufacturer (or an assembler) who collaborates transact, collaborate, communicate, and share information.
Enterprise
Systems ERP, SCM, KM
Analysis
CAD Drawings
Engineering Data Repository,
Systems Blueprints Data Warehouse BI, DSS, Workflow,
Bill of Materials
Intelligent Systems
Website Product/Process
Data Surfing Logs Displays,
Visualization,
Portal
Suppliers,
Product/service Component- Customers
design designers,
Government
Strategy Collaborate with
decision business Interactions Interactions
making partners
(suppliers,
customers,
distributors)
Manufacturers,
Assemblers,
Demand Retailers,
Supply chain visibility and Engineers,
visibility and forecasting Marketers, HRM,
planning Finance
The Process The Elements and Tasks
Figure 4.10 Elements and process of c-commerce systems