Page 32 - Introduction to Electronic Commerce and Social Commerce
P. 32
1.2 The Electronic Commerce Field: Growth, Content, Classification, and a Brief History 9
Electronic Commerce Applications
Direct Marketing Search Jobs Online Banking
E-government E-purchasing B2B Exchanges C-commerce Social Commerce
E-learning M-commerce Auctions Travel Online Publishing Consumer Services Collaboration 2.0
People: Public Policy: Marketing and Support Services: Business
Buyers, Sellers, Taxes, Legal, Advertisement: Order Fulfillment, Partnerships:
Intermediaries, Privacy Issues, Market Research, Logistics, Affiliate Programs,
Service, IS People, Regulations, Promotions, Payments, Joint Ventures,
and Management Compliance, and Web Content, Content, and Exchanges,
Technical and Security System E-marketplaces,
Standards Targeted Marketing Development and Consortia
Support Services
(1) (2) (3) (4) (5)
Common business Messaging and Multimedia content Network infrastructure Interfacing
service infrastructure information distribution and network (telecom, cable TV infrastructure
(security, smart infrastructure publishing infrastructure wireless, Internet, (with databases,
cards/authentication, (EDI, e-mail, hypertext (HTML, JAVA, VAN, WAN, LAN, business partners
electronic payments, transter protocol, chat XML, VRML) intranet, extranet) applications,
directories/catalogs, rooms) access, Wi-Fi, WiMax Web Services,
hardware, peripherals) Web 2.0 tools (cell phones) ERP)
Infrastructure
Management
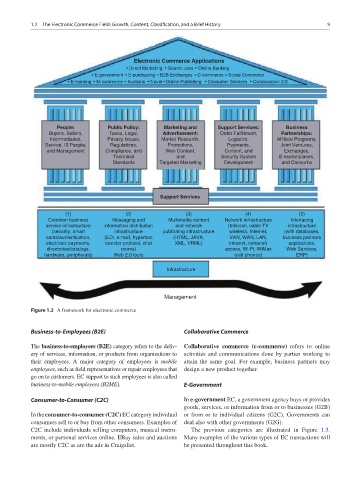
Figure 1.2 A framework for electronic commerce
Business-to-Employees (B2E) Collaborative Commerce
The business-to-employees (B2E) category refers to the deliv- Collaborative commerce (c-commerce) refers to online
ery of services, information, or products from organizations to activities and communications done by parties working to
their employees. A major category of employees is mobile attain the same goal. For example, business partners may
employees, such as field representatives or repair employees that design a new product together.
go on to customers. EC support to such employees is also called
business-to-mobile employees (B2ME). E-Government
Consumer-to-Consumer (C2C) In e-government EC, a government agency buys or provides
goods, services, or information from or to businesses (G2B)
In the consumer-to-consumer (C2C) EC category individual or from or to individual citizens (G2C). Governments can
consumers sell to or buy from other consumers. Examples of deal also with other governments (G2G).
C2C include individuals selling computers, musical instru- The previous categories are illustrated in Figure 1.3.
ments, or personal services online. EBay sales and auctions Many examples of the various types of EC transactions will
are mostly C2C as are the ads in Craigslist. be presented throughout this book.