Page 398 - Introduction to Electronic Commerce and Social Commerce
P. 398
386 12 Implementation Issues: From Globalization to Justification, Privacy, and Regulation
A number of different methods are available to measure However, even when formal analysis is not required, an
the business value of EC and IT investments. Traditional organization should conduct at least some qualitative analy-
methods that support such analyses are net present value sis to explain the logic of investing in the EC project.
(NPV) and ROI (see nucleusresearch.com/research).
Cost–Benefit Analysis and the Business Case Using Metrics in EC Justification
The cost–benefit analysis and the business value are part of a Metrics can be used to designate the ratio between costs and
business case. The business case’s cost benefit includes three benefits or the total costs or do comparisons. They are used
major components: Benefits (e.g., revenue increase, cost reduc- not only for justification but also for other economic activi-
tion, customer satisfaction), costs (investment and operating ties (e.g., to compare employee performance in order to
costs), and risks (e.g., obsolescence, employee resistance). reward those who do the best job). Metrics can produce very
Several vendors provide templates, tools, guidelines, and other positive results in organizations by driving behavior in a
aids for preparing the business case in specific areas. For number of ways. Metrics can:
example, IT Business Edge (itbusinessedge.com) provides
a Business Case Resource Kit (see itbusinessedge.com/
downloads).
• Be the basis for setting up specific goals and plans.
• Describe and measure the value proposition of busi-
What Needs to Be Justified? When Should ness models (Chapter 1).
Justification Take Place? • Align the goals of individuals, teams, departments,
and other organizational units with the enterprise’s
objectives.
Not all EC investments need to be justified formally. In some
cases, a simple one-page qualitative justification is sufficient. • Track the characteristics and/or performance of EC
systems, including usage, types of visitors, page vis-
The following are cases where formal evaluation may not be
needed: its, conversion rate, and so forth.
• Assess the health of companies by using tools such as
• When the value of the investment is relatively small for balanced scorecards and performance dashboards.
the organization.
• When the relevant data are not available, are inaccurate,
or are too volatile. Metrics, Measurements, and Key
Performance Indicators
When the EC project is mandated—it must be done regard-
less of the costs involved (e.g., when mandated by the govern- Metrics need to be defined properly with a clear way to mea-
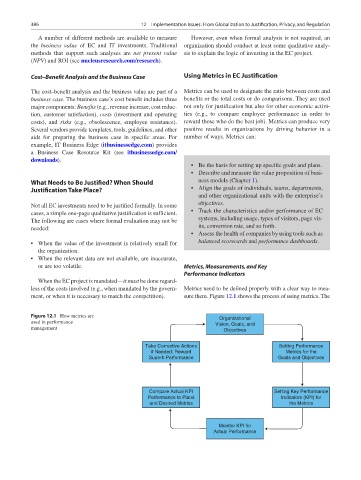
ment, or when it is necessary to match the competition). sure them. Figure 12.1 shows the process of using metrics. The
Figure 12.1 How metrics are Organizational
used in performance Vision, Goals, and
management Objectives
Take Corrective Actions Setting Performance
if Needed; Reward Metrics for the
Superb Performance Goals and Objectives
Compare Actual KPI Setting Key Performance
Performance to Plans Indicators (KPI) for
and Desired Metrics the Metrics
Monitor KPI for
Actual Performance