Page 45 - Introduction to Electronic Commerce and Social Commerce
P. 45
22 1 Overview of Electronic Commerce and Social Commerce
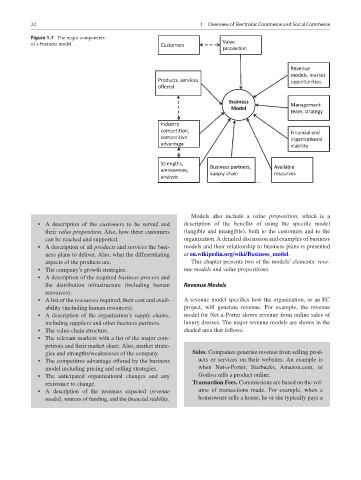
Figure 1.7 The major components
of a business model
Models also include a value proposition, which is a
• A description of the customers to be served and description of the benefits of using the specific model
their value proposition. Also, how these customers (tangible and intangible), both to the customers and to the
can be reached and supported. organization. A detailed discussion and examples of business
• A description of all products and services the busi- models and their relationship to business plans is presented
ness plans to deliver. Also, what the differentiating at en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Business_model.
aspects of the products are. This chapter presents two of the models’ elements: reve-
• The company’s growth strategies. nue models and value propositions.
• A description of the required business process and
the distribution infrastructure (including human Revenue Models
resources).
• A list of the resources required, their cost and avail- A revenue model specifies how the organization, or an EC
ability (including human resources). project, will generate revenue. For example, the revenue
• A description of the organization’s supply chains, model for Net-a-Porter shows revenue from online sales of
including suppliers and other business partners. luxury dresses. The major revenue models are shown in the
• The value-chain structure. shaded area that follows.
• The relevant markets with a list of the major com-
petitors and their market share. Also, market strate-
gies and strengths/weaknesses of the company. Sales. Companies generate revenue from selling prod-
• The competitive advantage offered by the business ucts or services on their websites. An example is
model including pricing and selling strategies. when Net-a-Porter, Starbucks, Amazon.com, or
• The anticipated organizational changes and any Godiva sells a product online.
resistance to change. Transaction Fees. Commissions are based on the vol-
• A description of the revenues expected (revenue ume of transactions made. For example, when a
model), sources of funding, and the financial viability. homeowner sells a house, he or she typically pays a