Page 473 - Introduction to Information Optics
P. 473
458 8. Information Storage with Optics
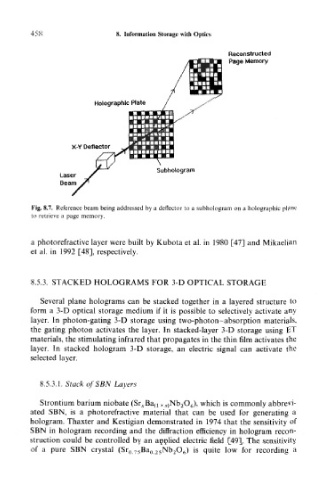
Reconstructed
Page Memory
Holographic Plate
X-Y Deflector
\
Subhologram
Laser
Beam
Fig. 8.7. Reference beam being addressed by a deflector to a subhologram on a holographic plane
to retrieve a page memory.
a photorefractive layer were built by Kubota et al. in 1980 [47] and Mikaelian
et al. in 1992 [48], respectively.
8.5.3. STACKED HOLOGRAMS FOR 3-D OPTICAL STORAGE
Several plane holograms can be stacked together in a layered structure to
form a 3-D optical storage medium if it is possible to selectively activate any
layer. In photon-gating 3-D storage using two-photon-absorption materials,
the gating photon activates the layer. In stacked-layer 3-D storage using ET
materials, the stimulating infrared that propagates in the thin film activates the
layer. In stacked hologram 3-D storage, an electric signal can activate the
selected layer.
8,5.3.1. Stack ofSBN Layers
Strontium barium niobate (Sr xBa {1 x JC)Nb 2O 6), which is commonly abbrevi-
ated SBN, is a photorefractive material that can be used for generating a
hologram. Thaxter and Kestigian demonstrated in 1974 that the sensitivity of
SBN in hologram recording and the diffraction efficiency in hologram recon-
struction could be controlled by an applied electric field [49]. The sensitivity
of a pure SBN crystal (Sr 0 75Ba 0 25Nb 2O 6) is quite low for recording a