Page 60 - Introduction to Mineral Exploration
P. 60
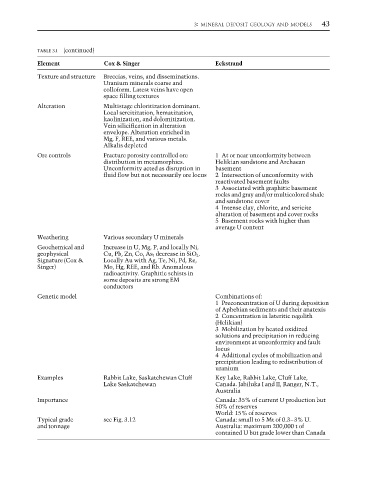
3: MINERAL DEPOSIT GEOLOGY AND MODELS 43
TABLE 3.1 (continued)
Element Cox & Singer Eckstrand
Texture and structure Breccias, veins, and disseminations.
Uranium minerals coarse and
colloform. Latest veins have open
space filling textures
Alteration Multistage chloritization dominant.
Local sercitization, hematization,
kaolinization, and dolomitization.
Vein silicification in alteration
envelope. Alteration enriched in
Mg, F, REE, and various metals.
Alkalis depleted
Ore controls Fracture porosity controlled ore 1 At or near unconformity between
distribution in metamorphics. Helikian sandstone and Archaean
Unconformity acted as disruption in basement
fluid flow but not necessarily ore locus 2 Intersection of unconformity with
reactivated basement faults
3 Associated with graphitic basement
rocks and gray and/or multicolored shale
and sandstone cover
4 Intense clay, chlorite, and sericite
alteration of basement and cover rocks
5 Basement rocks with higher than
average U content
Weathering Various secondary U minerals
Geochemical and Increase in U, Mg, P, and locally Ni,
geophysical Cu, Pb, Zn, Co, As; decrease in SiO 2 .
Signature (Cox & Locally Au with Ag, Te, Ni, Pd, Re,
Singer) Mo, Hg, REE, and Rb. Anomalous
radioactivity. Graphitic schists in
some deposits are strong EM
conductors
Genetic model Combinations of:
1 Preconcentration of U during deposition
of Aphebian sediments and their anatexis
2 Concentration in lateritic regolith
(Helikian)
3 Mobilization by heated oxidized
solutions and precipitation in reducing
environment at unconformity and fault
locus
4 Additional cycles of mobilization and
precipitation leading to redistribution of
uranium
Examples Rabbit Lake, Saskatchewan Cluff Key Lake, Rabbit Lake, Cluff Lake,
Lake Saskatchewan Canada. Jabiluka I and II, Ranger, N.T.,
Australia
Importance Canada: 35% of current U production but
50% of reserves
World: 15% of reserves
Typical grade see Fig. 3.12 Canada: small to 5 Mt of 0.3–3% U.
and tonnage Australia: maximum 200,000 t of
contained U but grade lower than Canada